• Surround Sound
over HDMI
• How
to hookup surround sound
TV Sizes
What
you should know about TV screen size
TV screen sizes range from 24 inch to over 100 inches with 65 in. becoming the standard for consumers.
How to decide what TV screen size to buy
1. Your budget size
2. Your room size
3. Your personal preferences
4. The weight of the TV
Your budget may be a consideration because as screen sizes increase so do the costs.
Your room size is a consideration due to viewing distances.
Also consider the weight of a TV. Larger screens tend to weigh more so handling, transport and mounting them can be an issue.
How to measure TV screen size
Place a tape measure in one corner of the screen, only the screen, not the TV frame itself. You want to measure only the viewing area, not the TV itself.
Now extend diagonally to the opposite corner and see how many inches it measures.
How
to calculate true screen size for a TV
When you look for a TV today, one of the first things you notice is
how they are designated by screen size. Most TVs are 32 inch, 40
inch, 46 inch, 50 inch or larger. But what exactly is this measurement?
It is the distance from one corner across to the opposite corner on a
diagonal. This is the standard way of designating screen size, a
diagonal line across the screen. But is this a true way to measure
screen size?
Someone who had a traditional analog TV with a 20 inch screen and
bought an HDTV with a 40 inch screen would assume that their TV screen
just doubled in size. But did it really? Lets take a closer look.
Simple math can be used to calculate true screen size for a TV.
First a small note to consider. TV screen sizes are not exact. A TV may
be designated as a 20 inch when in fact the screen is 20.5 inches
across or it could be 19.5 inches, close but not exact.
Calculate True Screen Size for a TV
Width
and height of TV screen
Measure the distance across the bottom of the screen (the screen only,
not the TV). This is the width of the screen. Now measure the distance
from the bottom of the screen to the top. This is the height of the
screen. To calculate the total screen area (total viewing area),
multiply the width times the height.
For example, if the TV screen
measures 16 inches wide and 12 inches high, then the total screen area
is 16 times 12 or 192
sq. inches.
192 sq. inches would be typical for an analog TV in the 20 inch size.
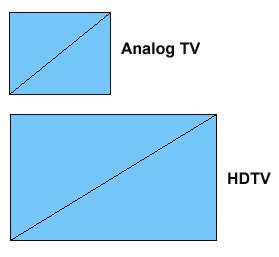
The screen size of this TV, 16 by 12, says a lot about what is known as
aspect ratio. The aspect ratio of traditional analog TV sets is 4:3 or
4 units wide by 3 units high and in our example we can see this is
true. 16 inches wide by 12 inches high is a 4 to 3 ratio. (Divide 16 by
4= 4 and divide 12 by 4= 3) or (Divide 16 by 12= 1.33) 4 to 3 is the
same as 1.33 to 1. This is how analog TV screens look, like a rectangle
but fairly close to a square.
HDTV screens on the other hand are much
wider than they are high. HDTVs have a 16:9 aspect ratio. 16 units wide
by 9 units high. Because HDTVs have this 16 to 9 aspect ratio,
comparisons to the old analog TV screens of the 4 to 3 aspect ratio are
like comparing apples and oranges.
But now lets look at the 40 inch HDTV. Measure the screen width and
then measure the screen height. A 40 inch HDTV screen measures roughly
40 inches at the diagonal. We can use math to make sure the
calculations are correct. For this example, the HDTV screen will
measure 35 inches wide and 19.7 inches high. This should be a 16:9
ratio. 16 to 9 is the same as 1.78 to 1 meaning the HDTV screen is 1.78
times as wide as it is high (divide 16 by 9= 1.78 and divide 9 by 9= 1)
or (divide 35 by 19.7= 1.78). Now to calculate total screen area,
multiply width times height or 35 times 19.7= 689.5
sq. inches.
Much bigger than the 192 sq. inches of the analog TV. In fact the total
screen area of the 40 inch HDTV is more than double, yes, more than
triple the size of the 20 inch analog TV. That's right, the 40 inch
HDTV has a total screen area of 3.59 times larger than the 20 inch
analog TV.
How to Calculate Viewing Distance
A formula for determining the optimal size TV based on how far you want to sit from the screen
divides the viewing distance by approximately 1.5 to 2. If your viewing area is 8 feet away from the screen,
an HDTV in the 60″ range will get you the optimal cinematic experience. This is for 1080p televisions.
6 feet viewing would be 6 times 12 equals 72 divided by 1.5 equals 48 inches so a 50 inch screen would be good.
8 feet viewing would be 8 times 12 is 96 inches divided by 1.5 equals 64 inches so a 65 inch screen would be good.
So for ten feet viewing, 10 times 12 is 120 inches divided by 1.5 equals 80 inches so a 75 inch screen would be good.
Nearly all new TV screens are 4k Ultra-high-definition TVs. An increasing number are 8K resolution screens.
The new 4K Ultra HDTVs have 4 times the resolution of the 1080p display. Remember your media source must be 4K to get 4K resolution on the TV.
For example, your 8K TV will only show you 8K resolution if your source is in 8K and currently there is very little 8K source media.
The 4K and 8K screens have smaller pixels than 1080p so pixelation is less of a concern. So you should possibly sit closer to the screen for the best
experience. The 1.5 to 2 number changes for the 4K and 8K screens to 1 to 1.5 to approximate the best TV size.
Interesting
math for TV screens
The Pythagorean Theorem was one of the earliest theorems known to
ancient civilizations. This famous theorem is named for the Greek
mathematician and philosopher, Pythagoras. The Pythagorean Theorem is
Pythagoras' most famous mathematical contribution. The Pythagorean
Theorem is a statement about triangles containing a right angle. The
Pythagorean Theorem states that:
"The area of the square built upon the hypotenuse of a right triangle
is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares upon the remaining
sides." In other words:
a² + b² = c²
Applying this to TV screens, anyone can check the validity of screen
measurements. By drawing a line diagonal across the TV screen, the
screen forms two triangles. The width is "A" and the height is "B" and
the diagonal is "C". So if you know the length of the diagonal or if
you know the length of the width and height, you can calculate the
remaining side. Since HDTVs have a 16:9 aspect ratio, you can check the
measurements.
In the example above for the 40 inch HDTV: "A" is 35
inches and "B" is 19.7 inches and "C" is roughly 40 inches. "A" becomes
35 times 35 or 1225. "B" becomes 19.7 times 19.7 or 388 and "C", the
screen's diagonal size, is stated as roughly 40 times 40 or 1600.
Therefore 1225 plus 388 equals 1613. So then the square root of 1613 is
40.16 which would be the exact diagonal measurement. Any simple
calculator has the square root key to give you the answer.
Compare
analog TV with HDTV of the same screen size
If you own a 32 inch analog TV and want to get an HDTV with the same
screen size, you may be surprised to find out you actually have lost
screen viewing area. That's right, an HDTV with a screen size of 32
inches has less screen size than an analog TV of the same screen size.
The HDTV has a 16 to 9 aspect ratio and the analog TV has a 4 to 3
aspect ratio. Even though both TVs have the same screen diagonal
measurement, the screen area is a little different. Let's calculate
this.
A 32 inch analog TV screen measures 25.6 inches wide and 19.2 inches
high and 32 inches across diagonally. The aspect ratio of 1.33 to 1 (or
4 to 3) is calculated as 25.6 divided by 19.2 which equals 1.33 and the
total viewing area is calculated as 25.6 times 19.2 or 491.52 square
inches. Checking against the Pythagorean Theorem, 25.6 squared is
655.36 and 19.2 squared is 368.64. Then 32 squared is 1024. 655.36 plus
368.64 equals 1024.
Now let's compare the HDTV with a 32 inch screen size. The 32 inch HDTV
is 28 inches wide and 15.7 inches high. Therefore the total viewing
area is 28 times 15.7 or 439.6 sq. inches. So the 32 inch HDTV has
51.92 sq. inches less viewing area than the 32 inch analog TV! (491.52
minus 439.6) So the HDTV screen is actually 10.6 percent smaller in
total viewing area.
Therefore when you buy an HDTV to replace your
analog TV, and you want to make sure you do not lose screen viewing
area, you need to buy an HDTV with a screen size slightly larger than
your analog TV. Always round up when close in size. HDTV screen sizes
run from 19 inch up to 65 inch and more but typically most sets are in
the range of 26, 32, 37, 40, 42, 46, 50, or 55 inches. Anything bigger
gets to be too much to handle and weigh too much, particularly with
Plasma displays. Organic LED HDTV screens may eventually solve those
problems however. So if you have a 27 inch analog TV, get at least a 32
or 40 inch HDTV.
Watching
older video on an HDTV - Screen size considerations
Watching 4:3 content on an HDTV (16:9) is not a good match but it can
be done. Older video, meaning anything before 1997, on broadcast TV,
VHS, Laser Disc etc. was generally 4:3 and showing this on a 16:9 HDTV
display results in a mis-match. 4:3 content was designed to be
displayed on a 4:3 TV, meaning an analog NTSC TV. When you try to show
this older video on an HDTV, certain compromises have to happen. Thus
the appearance of the "black bars". The black bars can appear on the
top and bottom (letterbox), left and right (pillarbox) or on all four
sides at once.
How to get
rid of black bars
Getting the black bars off your screen is usually a compromise and can
be done by stretching or expanding across your screen. Depending on how
your devices are designed, you should be able to adjust the aspect
ratio of the source (DVD player, cable box etc.) and/or the TV in order
to change the way the video is displayed. A DVD player for example
should have a setting for adjusting the aspect ratio (4:3 - 4:3 pan
scan - 16:9) and your TV should have a button on the remote control or
in a menu setting to adjust aspect ratio. It may be called focus,
video, zoom, picture, setting, full, display or any number of other
labels but functionally perform an adjustment so that the video can be
expanded to fill the screen.
The issue here is picture distortion. This
is the compromise. You sacrifice picture quality sometimes in order to
get rid of the black bars. Even newer video can produce black bars on a
TV if the video content was produced in a wider aspect ratio than 16:9.
In some cases, when the video was produced in a widescreen format,
wider than 16:9, it may be impossible to completely get rid of the
black bars.
Sometimes the adjustments seem counter-intuitive but just keep trying
combinations until you get what you want. For example a DVD in
widescreen format displayed on a 4:3 TV may need the 16:9 setting in
the player in order to show up on the TV without black bars. You may
have to drill down in the on-screen menus for the DVD player in order
to set the aspect ratio.
Also make sure the DVD is not playing while
making the adjustment. If the DVD was produced in or modified to 4:3
then it will fill the screen of a 4:3 TV. Some DVDs have both 4:3 and
16:9 available. One on a side. Flip the DVD over and you may find the
widescreen version. If the DVD cover says the aspect ratio of the movie
is 2.35:1 or 2.39:1 then you may have to live with some small black
bars as this is very widescreen. If you do not like black bars, try to
pick your DVD in a format appropriate for your TV. A non-widescreen DVD
would be better for an analog TV. If however you want to see the movie
as intended, widescreen is better, but you may have to live with the
black bars unless you expand the video, producing some distortion.
TV screen
sizes - calculating viewing
area for different viewing
modes
32 inch HDTV and 19
inch analog TV
Comparing a 32 inch 16:9 TV to a 19 inch 4:3 TV
32 inch 16:9 Set - 19 inch 4:3 Set
4:3 (1.33:1) NTSC mode [89.4% larger] - 4:3 (1.33:1) standard mode
Your viewing area is 20.9 in(w) x 15.7 in(h)
Total viewing area is 328.13 sq in.
This is the equivalent of a 26.1 inch 4:3 TV
Your viewing area is 15.2 in(w) x 11.4 in(h)
Total viewing area is 173.28 sq in.
16:9 (1.78:1) native mode [239.0% larger] - 16:9 (1.78:1) letterbox
mode
Your viewing area is 27.9 in(w) x 15.7 in(h)
Total viewing area is 438.03 sq in.
This utilizes the full display of the 16:9 TV
Your viewing area is 15.2 in(w) x 8.5 in(h)
The diagonal size is 17.4 in
Total viewing area is 129.2 sq in.
This is the equivalent of a 17.4 inch 16:9 TV
Your viewing area is decreased by 25.4% from 4:3 mode
16:9 (1.85:1) letterbox mode [238.0% larger] - 16:9 (1.85:1) letterbox
mode
Your viewing area is 27.9 in(w) x 15.1 in(h)
The diagonal size is 31.7 in
Total viewing area is 421.29 sq in.
Total area is 16.7 sq in. (3.8%) smaller than 1.78:1
Your viewing area is 15.2 in(w) x 8.2 in(h)
The diagonal size is 17.3 in
Total viewing area is 124.64 sq in.
Your viewing area is decreased by 28.1% from 4:3 mode
16:9 (2.35:1) letterbox mode [236.0% larger] - 16:9 (2.35:1) letterbox
mode
Your viewing area is 27.9 in(w) x 11.9 in(h)
The diagonal size is 30.3 in
Total viewing area is 332.01 sq in.
Total area is 106.0 sq in. (24.2%) smaller than 1.78:1
Your viewing area is 15.2 in(w) x 6.5 in(h)
The diagonal size is 16.5 in
Total viewing area is 98.8 sq in.
Your viewing area is decreased by 43.0% from 4:3 mode
40 inch HDTV and 27
inch analog TV
Comparing a 40 inch 16:9 TV to a 27 inch 4:3 TV
40 inch 16:9 Set - 27 inch 4:3 Set
4:3 (1.33:1) NTSC mode [46.2% larger] 4:3 (1.33:1) standard mode
Your viewing area is 26.1 in(w) x 19.6 in(h)
Total viewing area is 511.56 sq in.
This is the equivalent of a 32.7 inch 4:3 TV
Your viewing area is 21.6 in(w) x 16.2 in(h)
Total viewing area is 349.92 sq in.
16:9 (1.78:1) native mode [161.7% larger] 16:9 (1.78:1) letterbox mode
Your viewing area is 34.9 in(w) x 19.6 in(h)
Total viewing area is 684.04 sq in.
This utilizes the full display of the 16:9 TV
Your viewing area is 21.6 in(w) x 12.1 in(h)
The diagonal size is 24.8 in
Total viewing area is 261.36 sq in.
This is the equivalent of a 24.8 inch 16:9 TV
Your viewing area is decreased by 25.3% from 4:3 mode
16:9 (1.85:1) letterbox mode [161.0% larger] 16:9 (1.85:1) letterbox
mode
Your viewing area is 34.9 in(w) x 18.9 in(h)
The diagonal size is 39.7 in
Total viewing area is 659.61 sq in.
Total area is 24.4 sq in. (3.6%) smaller than 1.78:1
Your viewing area is 21.6 in(w) x 11.7 in(h)
The diagonal size is 24.6 in
Total viewing area is 252.72 sq in.
Your viewing area is decreased by 27.8% from 4:3 mode
16:9 (2.35:1) letterbox mode [161.7% larger] 16:9 (2.35:1) letterbox
mode
Your viewing area is 34.9 in(w) x 14.9 in(h)
The diagonal size is 37.9 in
Total viewing area is 520.01 sq in.
Total area is 164.0 sq in. (24.0%) smaller than 1.78:1
Your viewing area is 21.6 in(w) x 9.2 in(h)
The diagonal size is 23.5 in
Total viewing area is 198.72 sq in.
Your viewing area is decreased by 43.2% from 4:3 mode
50 inch HDTV and 32
inch analog TV
Comparing a 50 inch 16:9 TV to a 32 inch 4:3 TV
50 inch 16:9 Set - 32 inch 4:3 Set
4:3 (1.33:1) NTSC mode [63.0% larger] 4:3 (1.33:1) standard mode
Your viewing area is 32.7 in(w) x 24.5 in(h)
Total viewing area is 801.15 sq in.
This is the equivalent of a 40.9 inch 4:3 TV
Your viewing area is 25.6 in(w) x 19.2 in(h)
Total viewing area is 491.52 sq in.
16:9 (1.78:1) native mode [189.8% larger] - 16:9 (1.78:1) letterbox
mode
Your viewing area is 43.6 in(w) x 24.5 in(h)
Total viewing area is 1068.2 sq in.
This utilizes the full display of the 16:9 TV
Your viewing area is 25.6 in(w) x 14.4 in(h)
The diagonal size is 29.4 in
Total viewing area is 368.64 sq in.
This is the equivalent of a 29.4 inch 16:9 TV
Your viewing area is decreased by 25.0% from 4:3 mode
16:9 (1.85:1) letterbox mode [191.3% larger] - 16:9 (1.85:1) letterbox
mode
Your viewing area is 43.6 in(w) x 23.6 in(h)
The diagonal size is 49.6 in
Total viewing area is 1028.96 sq in.
Total area is 39.2 sq in. (3.7%) smaller than 1.78:1
Your viewing area is 25.6 in(w) x 13.8 in(h)
The diagonal size is 29.1 in
Total viewing area is 353.28 sq in.
Your viewing area is decreased by 28.1% from 4:3 mode
16:9 (2.35:1) letterbox mode [190.6% larger] 16:9 (2.35:1) letterbox
mode
Your viewing area is 43.6 in(w) x 18.6 in(h)
The diagonal size is 47.4 in
Total viewing area is 810.96 sq in.
Total area is 257.2 sq in. (24.1%) smaller than 1.78:1
Your viewing area is 25.6 in(w) x 10.9 in(h)
The diagonal size is 27.8 in
Total viewing area is 279.04 sq in.
Your viewing area is decreased by 43.2% from 4:3 mode
Recommended
viewing distances
For 4:3 TV displays, the standard for viewing distance is from 3 to 6
times the width of the screen. So if you have a 27 inch
screen, you can sit about 7 feet to 13 feet away.
But with HDTV,
you can sit closer to the TV set because it offers more detail than
analog TV. You can actually sit as close as 1.5 times times
the
screen’s diagonal size. The recommended maximum
viewing
distance is 2.5 times the screen size. So for a 40 inch HDTV, sit about
5 feet to about 9 feet away. If you feel more comfortable at a greater
distance by all means do what you think is best as these are just
general guidelines.
EYE STRAIN
Both very dark and very bright rooms can cause eye strain over time.
Also reflections off the screen caused by local lights, windows or
other light sources can cause difficult viewing.
|

