Home
TV Setup and Installation
TV: High Definition Setup
Guide
This TV guide will walk you through
the major steps of your TV installation.
How to Set Up a Smart TV
Wondering how to set up a smart TV? Here are the main steps you have to take in order to setup a smart TV:

Unboxing: Open the TV box and lift the TV out. For larger TVs, this could be a two person job. Set the TV on a soft flat surface. Remove any
protective coverings except leave the screen protection in place for now. Find the TV stand or legs and if not wall mounting, get a screwdriver
and attach the stand to the TV using the provided screws.

Some TVs have a pedestal stand while others use two legs.
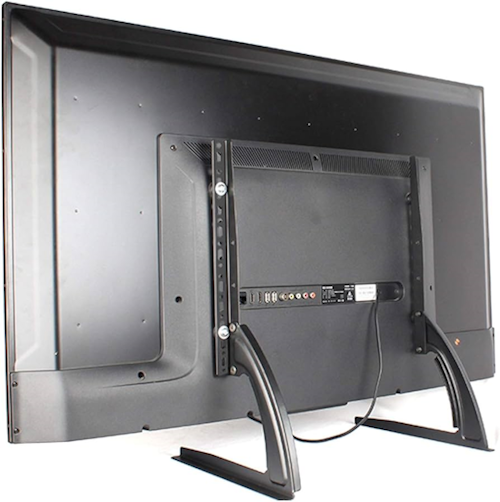

Choose the Perfect location for your TV
Wall mount or Stand - using the stand is simple while wall mounting is more complex. You may want to attach the stand first and wall mount later, after
the TV is checked and setup for the first time.
Lift TV upright and place on a hard flat surface on the stand with screen facing you. Remove any screen protector.
Attach the TV power cord and plug TV into power outlet and power ON

Insert batteries into TV remote control or be sure remote is fully charged.

TV Standard Remote

TV Smart Remote
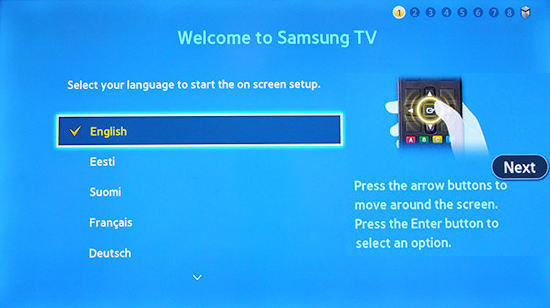
Every TV has different first steps. Some will ask for your preferred Language, others will ask if you want to use the TV remote or your phone.
Follow the process, selecting your choices with the TV remote or phone.

Connect your TV to the internet
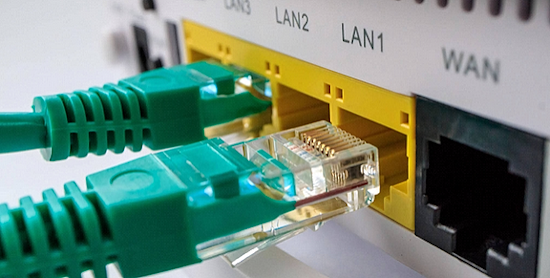
One of the common first procedures for TV setup is to connect to the internet.
Connect an Ethernet cable from TV LAN port to your router LAN port or use Wi-Fi.
When asked, choose your home network name from the list and enter your Wi-Fi password if going wireless to connect.
Update TV software
Next the Update TV software process may occur if your TV is not up to date with the latest code. This may take 10 mins. After completed, the TV
will restart with the new code installed.
To update without internet access, you can usually use a USB thumb drive and download to the drive, then insert USB drive into TV's USB port to install
the code.
Some TVs will ask you to create a user account with a password. You can skip this and do it later if preferred or you can create an account.
You can also sign-in to your existing account online if you have one using your phone.
Voice commands - Choose your assistant or skip for now.
Navigate the TV’s on-screen set up process and its settings
Master the device’s interface and home screen
Install your apps
Every TV has their app store where you can download apps which will run on that TV. Navigate to the APP icon and search for the app you want to get.
Remember that many apps are not free. You may need to sign up and pay before access is granted.
Connect External devices
Bluray/DVD player, Satellite TV, game consoles, streaming devices can be connected with HDMI cables to the TV HDMI inputs. A soundbar can be connected to
the TV HDMI eARC/ARC port for better sound.
Connect your Antenna
A VHF/UHF TV antenna connection using RG-6 coaxial cable will allow local broadcast channels to be received by the TV tuner. Use the round silver
threaded port on the TV marked ANT/Cable. Be sure to perform a channel scan to save local TV channels in the TV memory.
Go through the smart features
Troubleshoot common issues
Fine-tune your TV’s settings
Picture, Sound and other settings you may want to get setup using the TV menus will allow you to enjoy the content you want. Every TV has
different menu options but generally navigate to SETTINGS and from there, drill down to sub-menus to find the items you want to change.
TV Connections
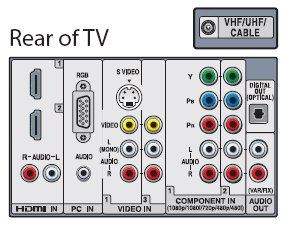
You are familiar with standard connections to your TV, such as from
your VCR, DVD player or satellite decoder. These include RF coaxial cable
connection, composite video (RCA Type), S-Video and Component Video.
Now with HDTV you will need to become familiar with some new digital
connections. The digital connections have pros and cons and your HDTV or
decoder/tuner box may not support them all. You should check the manual or
the rear of your HDTV set or tuner box to determine what connections are
supported. Many of the digital connections involve copy protection
capability to prevent content recording. This copy protection could be
used to prevent recording of Pay per view channels for example.
Connections:
VGA- VGA connections, also known as D-Sub-15,
have been around for many years in the computer world. The 15 pin VGA
connector is used to link a personal computer with its monitor. The analog
VGA connection is usually used on HDTV tuners to support a computer
monitor.
Component Video- The component video connection
is the most common way to connect HDTV set top boxes and HDTV cable or
satellite decoders to HDTVs. Component video separates the video signal
into 3 distinct streams (red, green and blue), in which the video signal
is carried via three individual cables using RCA type jack connections.
There are two types of component video, Y,Cr,Cb (normal interlaced DVD
players) and Y,Pr,Pb (Progressive scan DVD players, HDTV decoders and DTV
inputs on televisions). Separating the video stream prevents color bleed
and delivers an increase in picture quality compared to composite video
where the red, green and blue segments are compressed together into a
single channel.

HDMI- High Definition Multimedia Interface
(HDMI) is the newest connector and is the successor to DVI. HDMI
began appearing on new HDTV sets in late 2003. HDMI, unlike DVI, which can
only pass video, is capable of passing both video and multi channel audio
(up to 8 channels).
 
HDMI Cable and jack
HDTV Connections
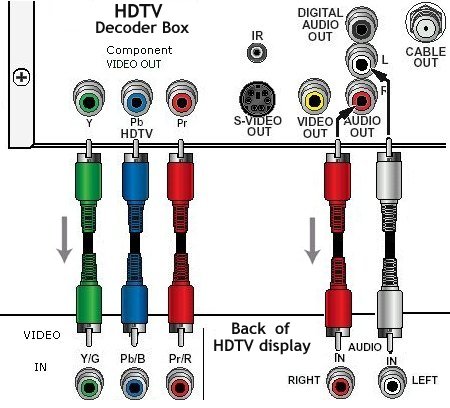
The most common way to connect your HDTV cable TV tuner box or HDTV
satellite decoder directly to your HDTV is to use a component video
connection. If both your set top box and HDTV support HDMI, you can use a
HDMI cable connection instead. HDMI keeps the whole connection digital where component video has to convert analog.
Some people opt to connect their multimedia devices to their television
through their audio/video receiver so as to allow the receiver to switch
between video sources. For high definition applications however, you will
need to consult your A/V receivers documentation to see if it supports
high bandwidth video connections. Your manual should refer to this as
"wide-bandwidth", "HDTV compatible" or "wideband".
If your A/V receiver is an older model, it is likely that it does not support
wideband video and you will not want to connect it in this manner or you
will be restricting the video resolution which reaches your HDTV. Also
ensure any additional cables, splitters and other devices are capable of
handling the full HDTV bandwidth. A bandwidth of at least 110Mhz is
required to transmit HDTV signals through it without degradation. Most newer A/V receivers support HDMI.
• See over 100 hook up diagrams
Audio Considerations
You should also consider your systems audio capability. Since many HDTV
and other DTV formats broadcast audio in Dolby Digital 5.1 (AC-3) or other
5.1 digital surround formats (DTS), you may wish to invest in an external
A/V receiver which is capable of decoding this audio format. At the very
least, you will want a receiver or television capable of decoding Dolby
Pro-logic, otherwise you will be missing out on the outstanding sound
fidelity that HDTV can deliver.
Most quality mid range to high end A/V receivers support both Dolby
Digital 5.1 as well as DTS and Dolby Pro-logic. Having all 3 standards is
important so you can receive full audio benefit with other media devices
such as DVD's, which sometimes use DTS instead of Dolby Digital. True
Surround Sound requires 3 front loudspeakers and 2 or 3 rear loudspeakers
as well as a subwoofer for bass. Most televisions only have 2 speakers at
best so you'll need to invest in an audio system for added sound
quality.
HDTV Setup
Now that you are familiar with the basics of high definition, you are
ready to begin setting up your system. Your first step is to determine
from your televisions manual if your set's native input is 720
progressive, 1080 interlaced or 1080 progressive.
This is important
as you will need to setup your HDTV receiver or decoder to match your
television.
Most HDTV sets come with a number of audio/video inputs allowing you to
connect your HDTV decoder in addition to your DVD player, satellite system
and other media devices. The television's video/input button allows you to
toggle between different sources.
- Choose the desired method of connecting your HDTV set-top-box to
your television. For most people, the component video connection
combined with the digital audio coaxial or optical TOSLink cable works
very well. You can also use one of the alternate methods described
earlier if you so choose, if they are supported by both your television
and set top box.
- If you also have an audio receiver, you will want to connect this to
your HDTV set top box as well. If your box supports more than one set of
audio outputs, you likely will want one set going directly to your
television, and another set going to your audio video receiver. In this
fashion, you will be able to listen to audio through both your
television speakers and also through your audio video receiver. This is
handy if you don't want to have to turn on your audio receiver every
time you want to watch television.
- Setup your set top box to match your television native HDTV video
mode, 720 progressive or 1080 interlaced or 1080 progressive. Some
set top boxes have a switch located at the back and others have a menu
setting which performs this function thru the remote control.
- Now you must setup your HDTV for the first time. You should consult
with your operating manual as most sets have an on-screen menu which can
assist you with this task. This allows you to configure the connections
that you are using as well as tuning the television for off-air
reception, audio connections and more. It should also be calibrated as
well for correct color, contrast, brightness and other critical
settings.
- Check that the aspect ratio is set to 16:9 preferred, or "full
screen mode" on your television, set top box and DVD player. If a
broadcast is not available in 16:9 it will automatically revert to 4:3.
Most recent mid range to high end televisions also now have the
capability to "zoom in" or "stretch" a 4:3 ratio broadcast to fill most
of a wide screen picture, although there will be a noticeable picture
distortion or loss of some top and bottom details with 4:3
broadcasts.
- If you are using an off-air HDTV decoder, you will want to setup the
decoder for your antenna. Most decoders have an on-screen digital signal
meter where you can adjust your antenna for optimum signal strength.
Remember, unlike an analog signal which can deliver a "snowy picture" in
fringe area, with digital you either will receive a perfect signal or
none at all, however homes in rural areas will require a larger outdoor
antenna to receive an adequate signal. Off-air HDTV signals utilize the
UHF band, which is much more limited in range than VHF, so you will need
an antenna with a good UHF range or one specifically designed for HDTV
reception.
- Proper placement of your television is also important as well,
especially if you have purchased a rear projection screen television
where viewing angle is critical. You will generally want to match the
screen size to the size of the room. For example a 57" television is a
poor match for a 6'x6' living room. A general rule of thumb for
determining a comfortable viewing distance is 2x the diagonal screen
size, so for a 40" television, a good comfortable viewing distance is
about 6 to 10 feet from the television. You will also want to
determine if room lighting will affect your viewing as well. Projection
screen televisions are far more easily "washed out" by sunlight than
direct-view televisions, so you will want to make sure you can close the
curtains or blinds to reduce this in bright sunlight conditions. Lamps
and lights should not reflect on the screen during night viewing, so
move lamps away from the viewing screen to maximize viewing enjoyment.
- One more option to consider is calibrating your HDTV. Calibration involves adjusting contrast, brightness, color saturation, and other settings so that your HDTV
performs up to its full potential and you view video as intended. You can do it yourself with a calibration DVD such as Avia or Digital Video Essentials, or you can opt to have a ISF certified professional make the adjustments for you. The ISF website has listings for your state and area so you can contact local technical people to perform this service. The cost is around $300.
HDTV Recording Considerations
Recording high definition broadcasts is also an important
consideration, since it cannot be recorded via conventional means such as
VCR or regular personal video recorder without loss of the
HD picture quality.
Many HD cable TV decoder set-top-boxes have the capability to record High
Definition broadcasts. Many satellite TV decoders also have the capability to
do this. More and more manufacturers will be introducing equipment for
this purpose as HDTV broadcasts become commonplace.
Mainstream DVR manufacturers such as Tivo have HDTV compatible
models. It is important to remember that the high bandwidth
nature of high definition broadcasts will significantly reduce your
recording capacity as they consume many times the amount of storage space
compared to standard broadcasts. Larger capacity hard drives are being
introduced to help solve this issue.
Another method of recording HDTV broadcasts is over a FireWire/IEEE
1394/iLink connection if your Set top box supports it.
In order to record over the FireWire connection, you will also need a
digital VCR (D-VHS), which can also playback broadcasts over the
connection. Digital VCR's are also capable of playing and recording analog
sources such as regular VHS tapes.
If you lack HDTV capable DVR or DVHS/FireWire connection, you can also
record a down-converted version of the HDTV broadcast over the analog
S-Video/composite audio/video connections. This would allow you to make
use of your analog VCR or Tivo or other DVR device. The broadcast will be
in either Enhanced Definition Television format (EDTV), or the Standard
Definition format (SDTV), which is limited to 480 lines of resolution,
delivering near DVD quality.
The newer Blu-ray Disc formats
will allow High-Def recording to optical disc.
HDTV
cable connection diagrams : TV
display types
Audio
Video connections : Cable
connections
How do I know a TV is a HDTV
Columbia ISA Audio Video
columbiaisa@yahoo.com
Empowering consumers through information.
|


