Audio
Video Cables and Connections
Audio Video Connection Types
• Cables
| Analog or Digital |
Audio and video information is combined and
carried on a single wire. RG-59 or RG-6 cable.
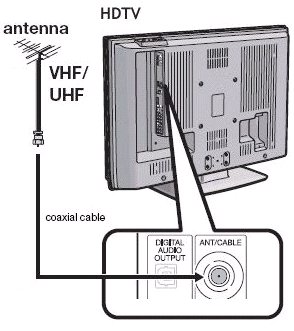
Satellite and Cable TV, Over-the-Air TV Antenna. 75 ohm. |
| RF coaxial "F" Type - USA |
  |
| Analog or Digital |
Audio / Video
Audio and video information is combined and
carried on a single wire. The Belling-Lee plug is widely used in Europe as a TV connector, commonly known as a TV aerial plug.
Used for digital terrestrial TV (Enfield Belling Lee company 1922). |
RF
coaxial United Kingdom |



 |
| Analog |
Audio only
2-channel Stereo.
Left channel (white) and right channel (red)
CD players, DVD players, tape cassette decks, Turntables |
RCA |
  |
| Analog |
Audio only
Guitars, Amps, Headphones, analog audio inputs/outputs |
TRS
Tip
Ring
Sleeve
1, 2, 3 or 4 poles |
 |
| Analog |
Audio only
Amplifier to Loudspeakers |
Speaker Wire
• Bare Wire
• Banana Plugs
• Spade
• 12, 14, 16 AWG |


 |
| Digital |
Audio
Multi-channel Bitstream or PCM.
(Surround sound after decoding)
Typically color coded black or orange. Capable of up to 5.1 surround sound. (Dolby Digital) |
RCA |
  |
| Digital |
Audio
Multi-channel Bitstream or PCM.
(Surround sound after decoding)
An optical
digital connection sends signals
in the form of light, as opposed to electrically. Optical cables have
the advantage of being immune to
EM (Electro-Magnetic) and RF interference. Capable of up to 5.1 surround sound. (Dolby Digital) |
Optical
Toslink
SPDIF |

 |
| Analog |
Audio
Surround Sound (Dolby Digital 5.1)
Six channel sound, left, right, surround left, surround right, center
channel and low frequency effects. Devices which do their own internal
decoding send the analog audio via a RCA cable. |
RCA |
 |
| Analog |
Audio
XLR Balanced Audio. The term “XLR” stands for External Line Return, and these cables consist of three pins arranged in a triangular configuration,
with one ground wire and two signal carriers. The signal pins carry a reverse polarity copy of the signal, effectively
cancelling out interference signals and delivering a clean signal that enhances sound quality. Used in the professional audio industry, facilitating
the transmission of balanced audio signals between microphones, mixers, and amplifiers.
They gained popularity due to their ruggedness, reliability, and ability to minimize interference and signal noise. |
XLR
3 Pin |




XLR cable
locking design |
| Analog |
Audio
SpeakON (Neutrik Speakon) connectors are for high-power speaker-level connections (amp to passive speaker) with secure,
twist-lock designs, high current handling (up to 25A), and thicker wire capacity, preventing accidental disconnects. Mostly used in
professional audio systems, there are 2, 4 or 8 contacts designs.
XLR connectors on the other hand, are for balanced, low-level signals (microphones, line-level audio)
with a 3-pin balanced connection, noise resistance, and a simple latch, not speaker power. |
SpeakON - To connect, insert the plug and rotate it clockwise until it clicks into place. To disconnect, press on the cable's button and
rotate counter-clockwise for half a circle before pulling out. |
Speakon
Male connector

Internal 4-wire

Female connection

|
| Analog |
Video
Composite
All video information is combined and carried on a single cable.
Typically color coded yellow. Capable of 480i and 480p. |
RCA |
  |
| Analog |
Video only
S-Video
brightness and color information is carried on separate wires giving
better picture results than composite video. Capable of 480i and 480p. |
4-pin |

 |
| Analog |
Audio and Video
SCART
Europe 1977 to 2002 TVs, VCRs, DVD players.
Video: composite, S-video, RGB. Stereo audio.
|
21-pin |


 |
| Analog |
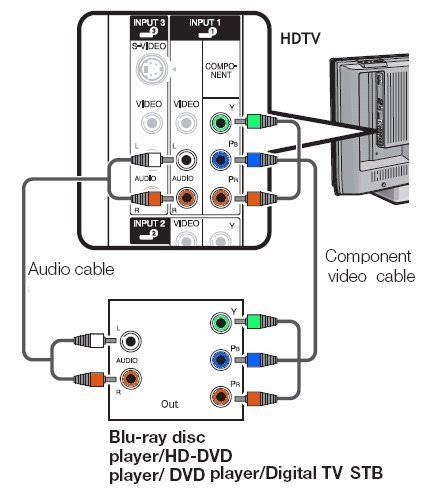
Video
Component
Video information is carried on 3 separate cables allowing brightness
and color information to be processed independently giving better
picture quality than composite or S-video.
Breaks the video signal down into base components that include Y
(Luminance), Cr(Red Chromanance), and Cb (Blue Chromanance). This further separation
allows for the highest resolution analog signal pass through, with true
color reproduction. Capable of 480i, 480p, 720p, 1080i and 1080p. |
RCA |
  |
| Digital |
Audio / Video
Firewire or i.Link
FireWire is a cross-platform implementation of the high-speed serial
data bus -- defined by the IEEE 1394-1995, IEEE 1394a-2000, and IEEE
1394b standards -- that can move large amounts of data between
computers and peripheral devices such as digital camcorders. It
features simplified cabling, hot swapping, and transfer speeds of up to
800 Mbps (on machines that support 1394b). |
6-Pin
or
4-Pin
IEEE-1394
FireWire was largely discontinued as a standard interface in computers around 2012. While some devices, like the Thunderbolt Display, still had FireWire ports, they were discontinued by Apple in 2016.
USB largely replaced Firewire. |


6-Pin


4-Pin |
| Digital |
Video only
VGA
Standard computer monitor connection. Also found on older TVs for hookup to
computer. |
15-Pin
D-Sub |
 |
| Digital and Analog |
Video only
DVI
(Digital Visual Interface) offers a high-bandwidth, digital-to-digital
video connection. Capable of 480i, 480p, 720p, 1080i and 1080p. |
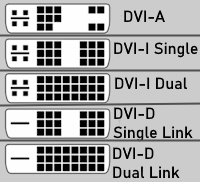
Multi-Pin
DVI
DVI comes in three main types: DVI-D (Digital only),
DVI-A (Analog only), and DVI-I (Integrated, both Digital & Analog),
with digital versions further split into Single Link (up to 1920x1200) and Dual Link (higher resolutions like 2560x1600). |

 |
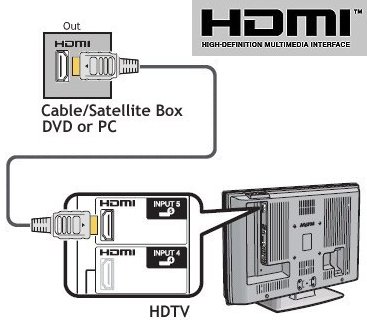
| Digital |
Audio and Video
HDMI
High
Definition Multimedia Interface. Video and multi-channel digital audio
transmission. It offers greater bandwidth than DVI, enabling it to
transmit high-definition uncompressed digital video signals. Capable of
480i, 480p, 720p, 1080i, 1080p, 4K and 8K. Capable of Dolby Digital Plus or Dolby TrueHD with Dolby Atmos. |
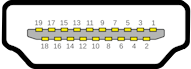
Multi-Pin
HDMI
19 Pins
TV, DVD, Bluray, Soundbar, Audio Video Receiver, Cable and Satellite TV Receivers.
There are also HDMI Mini (Type-C) and HDMI Micro (Type-D) sizes. The HDMI micro still maintains the 19 pin configuration.
|

HDMI Type-A
• What
is HDMI?
HDMI Micro Type-D


|
| Digital |
Audio and Video
DisplayPort and Mini DisplayPort
VESA standard. Video capable of 4K, 8K, 10K.
Mini DisplayPort developed by Apple Corp. 1080p, 4K, 8K.
|
Multi-Pin
DisplayPort
20 Pins |


 |
| Digital |
Video
Thunderbolt
Apple and Intel. Video 4K, 8K. Thunderbolt 1 and 2 use the same connector
as Mini DisplayPort, but Thunderbolt 3, 4 and 5 use the USB-C connector. Thunderbolt 3 uses a USB-C style plug and offers 40Gb/s in speed.
Video: 4K @ 120 Hz (single display).
It includes support for USB 3.1 and DisplayPort 1.2.
Thunderbolt 4 Video: 8K @ 60 Hz (single display)
4K @ 60 Hz (dual display).
|
Multi-Pin
Thunderbolt
20 Pins |



USB-C port |
| Digital |
Audio / Video
USB
Universal
Serial Bus for high-speed digital data transfers. |
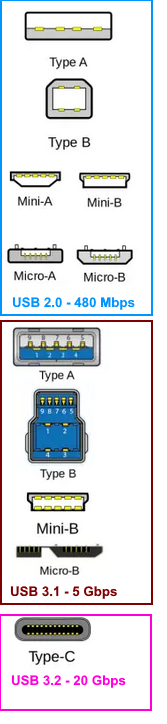
Multi-Pin
USB
USB Type C (USB-C) can deliver power, data, audio and video on a single cable.
A standard USB-C connector has 24 pins, arranged in two rows of 12,
however, cost-reduced cables and devices might use fewer pins (like 16 or 12) for basic charging
so not all USB-C cables have the same pin count or function. |
 |
| Digital |
Audio / Video
CAT5, CAT6 Ethernet
high-speed digital data transfers. LAN port - internet |
Multi-Pin
Ethernet
Routers, Modems, TVs, computers, networks |
  |
The following chart shows the various cable connection types which can
be made between audio and video components. Starting at the top and
progressing down, it shows the older, less sophisticated connection
types down to the newer, digital connection types. These cables and
connectors will connect analog TV, digital HDTV, DVD, Stereo, Home
Theater, and other similar hardware.

RS-170
Cable; RG-59
and RG-6
RF (radio frequency) F-Type connector coaxial cable.
Standard
audio/video TV/VCR/Cable-TV
connection.
Analog audio and video is
transmitted.


|
|
|
RF coaxial cable
EIA/TIA-170
Electrical Performance Standards - Monochrome Television.
EIA/TIA-170A
NTSC standard used for color television.
Video standard for an Unbalanced, 75 ohm (+/- 10%), Point-to-Point,
Coax (Cable) interface.
Standard interconnect for analog TV and VCR. Cable TV connection and
satellite
TV (RG-6) feed.
More...
|
|
AUDIO
CONNECTIONS


Analog audio
only
is transmitted
VIDEO CONNECTIONS


Analog video
only
is transmitted
|
|
|
RCA
Audio cables
RCA connections are the standard means of passing analog line-level
audio signals between components. RCA jacks are commonly found on most
types of Audio/Video gear.
The audio inputs and A/V inputs found on receivers are RCA connections.
Usually, RCA jacks, connectors and cables are grouped in stereo pairs,
with one connection for the left audio channel (white) and one for the
right audio channel (red). However, some components use a
single mono RCA jack (black) for audio input and/or output.
RCA Video cable
A composite
video input or output uses a
single standard RCA-style jack (yellow) to pass video signals. This
type of connection combines chrominance and luminance information,
sending it along a single cable. Though capable of delivering a
high-quality picture, composite video is not as accurate as either
S-video or component video, both of which provide separate paths for
chrominance and luminance.
Commonly found on A/V components like DVD players, VCRs, TVs, DBS
systems, etc., composite video jacks are often grouped with
corresponding stereo audio jacks (the composite video jack is usually
yellow). Though they use standard RCA-type connectors, composite video
cables are specially designed to maximize video signal transfer.
|
| |
|
|
|

Digital audio
only
is transmitted |
|
|
Digital
Audio
RCA
style coaxial
cable or Optical (Toslink)
cable transmits digital audio to decoder for eventual output. The
TOSLINK connection is audibly indistinguishable from coaxial S/PDIF. |

Coaxial RCA style cable

Optical cable |
|
|
Used on DVD players,
recorders, digital
cable/satellite boxes and Audio/Video receivers. (Dolby Digital and DTS
audio surround sound bitstream). TOSLINK, or more properly EIAJ
optical, signals have exactly the same format as the electrical S/PDIF
signals except, instead of using high/low voltages on copper to
represent the binary 1's and 0's of digital information, TOSLINK
utilizes a series of on/off pulses of a red transmitting light.
Contrary to popular belief, there are no lasers used in audio optical
digital transmission. The light source is a simple and inexpensive LED. |
|
|
|
|
|

Composite
Video
Cable
with stereo audio cables
|
|
|
Composite Video
Single "Yellow"
(shielded) RCA jack, which is not to be confused with the Audio (Red
and White) jacks of the three cable designs, or just a single black
cable in the older (1960-1970) audio connections.
Composite Video because it's a composite of the black-and-white
information (Y) and the color information (C) transmitted over
one cable.
(S-Video is better than Composite Video, and Component Video is better
than either of them.)
Found on all DVD players. |
|
S-VIDEO

S-video
cable
Analog Video only is transmitted

S-Video jack
|
|
|
S-Video
Alternative video
connection to composite
video, S-Video
[Super-video] sends video signals over a multi-wire cable, dividing the
video information into two separate [75 ohm coax or twisted pair
cables] signals: one for luminance (Light) 'Y' and one for chrominance
(Color) 'C'.
Each signal is sent shielded, enclosed in a 4-pin Mini-DIN.
S-video is used primarily with Hi8, S-VHS, MiniDV camcorders,
VCR, TV,
audio/video receivers and DVD players/recorders.
|
|

S-Video
Pin
Assignments
|
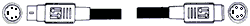
S-Video
Cable and
Connector Pinout
|
|
COMPONENT
VIDEO
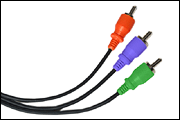
Component video
cable

Analog Video only is transmitted
|
|
|
Component Video
Component
Video is also called YPbPr,
or YCbCr
and transmits the picture information in a luminance and phase-opposite
chrominance pair over three coax cables [Red, Green, and Blue].
RGB
[Red, Green, Blue] is sometimes also called Component Video, but
combine the color, black and white signal.
YPbPr
is 'sometimes' used when discussing the three-wire analog video
component interface EIA-770 [EIA-770.2-a SMPTE-240M and others]. The
luminance (Y) is represented separately from the color components (Pb
and Pr).
In some cases The Y output is provided as a Green jack, the Pb is
provided as a Blue jack, and the Pr is provided as a Red jack. The 'Y'
signal carries the black and white information, The 'Pb' and 'Pr'
signals carry the color difference signals.
YCbCr
is used when discussing a digital component interface ITU-601 or
ITU-656 digital interfaces (formerly CCIR-601, CCIR-656). Y
is Luminance, Cb
is Blue Chromanance, and Cr
is Red Chromanance.
RGB
is the component format in which the primary colors (red, green, and
blue) are transmitted as three independent components. The color, black
and white signals are combined within these three signals. Only using
RGB inputs requires separate horizontal and vertical sync inputs. RGB
presents a better [TV] signal than the other forms of Component video,
S-Video, Composite Video, or RS-170. RGB sends each signal on a
separate cable and does not mix the color signals.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DVI
Digital Video

DVI
cable

DVI Jack
Found on HDTV, DVD
players and computer video cards
|
|
|
DVI
DVI:
Digital Visual Interface
Digital Visual
Interface .. standard for high-speed, high-resolution digital displays.
Developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG).
Digital Video Broadcasting/Digital Audio-Visual Council (DVB/DAVIC),
developed by DAVIC and DVB and adopted by European Telecommunication
Standards Institute (ETSI) and International Telecommunication Union
(ITU)
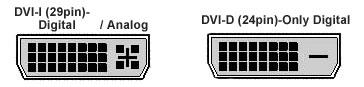
DVI has a number of different types connectors:
DVI-D
Digital only connector; 24 pins [modified D style];
DVI-I
Digital and Analog
[RGB]; 29 pins [modified D style]
DFP
Digital only connector
Digital Visual
Interface.
A data transmission port which supports up to 5 Gigabits/sec speed.
Bandwidth of
2.2 Gigabits/sec. is required to support uncompressed HD video
transmission.
With bandwidth of up to 5 Gbps for a single DVI link, compared to the
400
Megabits/sec. supported by IEEE 1394.
DVI also has the bandwidth to support higher audio fidelity, such as
more
channels of surround sound or 96 KHz sampling rates, as well as higher
video
resolution such as 1080p, ensuring less risk of long-term
obsolescence.
There are three different DVI configurations: DVI-A, designed for
analog
signals, DVI-D, designed for digital signals, and DVI-I (integrated),
designed
for both analog and digital signals.
More...
|
DVI
Connector
|
HDMI
Digital Video and Audio

HDMI
CABLE
video and audio are transmitted.

HDMI
JACK
|
|
|
HDMI
High-Definition
Multimedia
Interface™
Cable.
HDMI uses a smaller connector than the DVI connector. The specification
handles high-bandwidth, uncompressed video and multi-channel digital
audio as well, all in one cable. HDMI supports HDTV formats (720p,
1080i) with bandwidth to spare for future enhancements.
Found on HDTV, DVD players and home theater
receivers.
more...
|
| |
|
|
|
FIREWIRE
Digital Video and Audio

IEEE-1394
4-pin cable
(iLink or Firewire)

IEEE-1394
jack (4-pin)
Increasingly found on digital cable TV converters and set-top-boxes,
HDTV, DVD recorders and DVD-Audio/SACD Universal players and high-end
audio/video receivers.
FireWire is a new feature on HDTVs, but it's been around for a number
of years in the computer arena. FireWire connectors come in 4-pin and
6-pin configurations.
Unlike DVI, which was designed for one-way transmission of digital
video, FireWire is a two-way connection that can be used to route both
audio and video. FireWire establishes communication between multiple
devices linked on a home network, and the compressed MPEG-2 signals
that it carries can easily be recorded on digital videotape or
hard-disk recorders.
FireWire connections on digital TVs and set-top boxes support a
copy-protection scheme called DTCP (Digital Transmission Content
Protection) that's considerably more flexible than the HDCP scheme used
for DVI. With DTCP, a movie transmitted in high-def over satellite or
cable could be embedded with specific instructions that allow a digital
VCR to make one, several, or unlimited copies of the program. But for
premium content like pay-per-view movies where greater security is
desired, codes could be used to block recording altogether.
|
|
|
FireWire
(Apple) or i.Link
(Sony) is a high-speed serial bus that allows for the connection of up
to 63 devices. It is widely used for downloading video from digital
camcorders to a personal computer or DVD recorder. Also known as the
IEEE 1394 standard, the i.Link connector and the High Performance
Serial Bus (HPSB), the first version of FireWire supported 100, 200 and
400 Mbits/sec data transfer rates and a distance of 4.5 meters between
devices.
IEEE 1394b provides
800, 1,600 and 3,200 Mbps speeds, increases cable distance to 100
meters and can use glass or plastic fiber and Cat 5 Ethernet cable.
FireWire 800 was the first implementation of 1394b and became available
in 2003. Backward compatible with FireWire 400, earlier devices run at
the lower speed.
FireWire
Connectors
The 6-pin socket is commonly found on desktop computers. A 4-pin
version is used on laptops and audio/video devices. The faster FireWire
800 requires a 9-pin connector. Almost all modern digital camcorders
have included this connection since 1995. FireWire is used on the Apple
iPod music player.

6 pin Firewire jack
Sony's
implementation of the IEEE-1394 is known as i.Link, and uses only the
four signal pins, discarding the two pins that provide power to a
device.
|
Computer
Video

15 pin VGA jack found on some HDTV rear panels for hookup to a
computer. |
|
|
Used on personal computers,
this
connection can carry video image data in a variety of formats and
resolutions, and is often labeled according to these formats (VGA, SVGA
and XGA are the most common 4:3 formats; WVGA, WSVGA and WXGA are their
widescreen counterparts). RGB connectivity is becoming increasingly
common on high-end TVs as well, facilitating what's commonly referred
to as "digital convergence": the integration of formerly separate
systems (such as your PC and your home entertainment system) via a
single common display device. In other words, you can now compute using
your TV as a monitor (and your home theater audio system instead of
computer speakers). |
|

Back panel of
A/V
device showing various connectors
from
left to right-
PC audio miniplug, PC monitor input, headphones, S-Video,
composite video (yellow), analog audio (white & red),
component video (green, blue, red), analog audio (white &
red),
75 ohm RF coaxial cable input (silver),
12V DC
|
Audio
connections
Home
Theater Receiver Guide
PC
to HDTV hookup connection |
|
|
Video
connections
Cable
diagrams
See
over 100 hookup diagrams |
|