
 |
| Surround
Sound
:: DVD
Sound
Surround Sound Formats What Is Surround Sound? Surround sound refers to the use of multiple audio tracks to envelop the movie watching or music listening audience, making them feel like they're in the middle of the action or concert. The surround sound movie soundtrack allows the audience to hear sounds coming from all around them. Surround audio is stored in standard digital audio formats, encoded and then decoded on playback. Audio information is often compressed digitally to save space but also can be in an uncompressed digital format so that you get the original audio as recorded. Where does the surround sound come from? True surround sound formats rely on dedicated speakers that literally and physically surround the audience. 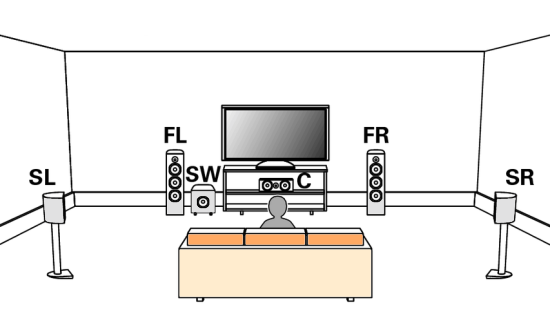 There is a center speaker which carries most of the actors dialog, and part of the soundtrack. There are left and right front speakers that carry most of the soundtrack (music and sound effects), and may carry parts of the dialog (when the director wants to intentionally off-set the source of the dialog to either side, from its default dead-center screen location). Then there is a pair of surround sound speakers that are placed to the side (and slightly above) the audience to provide the surround sound and ambient effects. Finally, a subwoofer can be used to reproduce the low and very low frequency effects (LFE) that come with certain movies. Surround Sound Sources Multiple audio tracks such as 5.1 are found on commercial DVD movie discs and Blu-ray discs. Digital TV broadcasts and internet streaming services can offer surround sound content. Some video games can offer surround sound. Cables To connect a DVD player or TV to the surround sound processor such as an Audio Video Receiver with loudspeakers, you would use HDMI cable (best) or Optical audio cable (good) or an RCA coaxial digital audio cable (good).   Connection diagram - Surround Sound 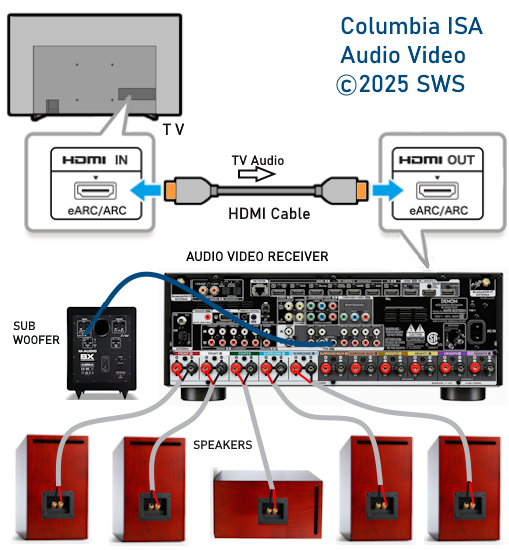 MONO If you use one microphone to record sounds, you get MONO or one audio track. A mono audio track would be played back to one speaker. You listen to the entire recording, all sounds, from one speaker placed in one location.  Mono record player with one analog audio track and one speaker STEREO If you use two microphones to record sounds, you get STEREO or two audio tracks, left and right. Stereo audio tracks would be played back to two speakers, a left speaker and a right speaker placed in two different locations. Stereo gives you a more realistic and a richer sound field more like actually being at the music performance.  SURROUND SOUND If you use three, four, five, six or more microphones in different locations to record sounds, you get SURROUND SOUND or multiple audio tracks. So you see that the amount of audio information gets larger and larger depending on the number of microphones in use. Surround sound is usually created in a studio where all the tracks are MIXED and designated to each separate channel/speaker for playback.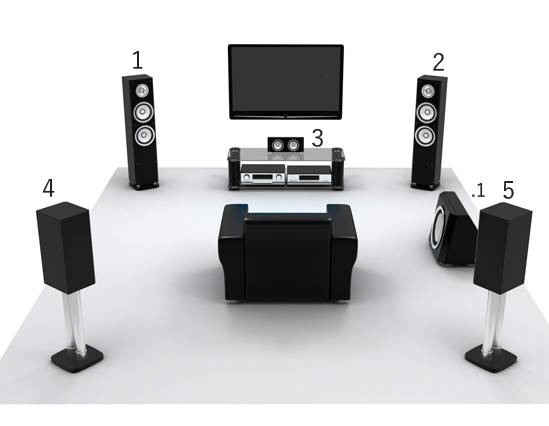  Surround Sound Setup - Standard 5.1 Standardized Formats for Surround Sound Dolby Digital™
Not
only is Dolby Digital the standard for DVD-Video, but it is also part
of the High Definition TV (HDTV) standard. It is used in
pay-per-view movies and digital TV channels of digital satellite
broadcasting (e.g., DIRECTV system). Readers
should note that not all Dolby Digital soundtracks have 5.1 channels of
audio. Those that are have the designation "Dolby Digital
5.1". Since Dolby Digital is a flexible surround sound format
that supports up to
5.1 channels, Dolby Digital soundtracks could have one channel of audio
(mono, designated as "Dolby Digital 1.0"), two channels of audio
(stereo or Dolby Surround Pro-Logic,
designated as "Dolby Digital
2.0"), or five channels of audio (designated as "Dolby Digital
5.0"). In fact, the Dolby Digital 2.0 soundtrack is required
for all Region 1 (U.S. and Canada) DVDs. DTS Digital Surround™
The primary advantage of DTS is that it offers higher data rates than Dolby Digital, leading many home theater enthusiasts to claim that DTS is better than Dolby Digital in sound quality. The down side is that a DTS soundtrack uses more of the disc's data capacity due to its higher data rate. This fact plus the fact that DTS is not a standard soundtrack format for DVD-Video makes DTS an optional 5.1-channel surround format that is actually available on few DVD-Video movies. There are far more DVD-Video titles with Dolby Digital soundtracks than there are those with the DTS surround sound format. Surround Sound systems with 6.1, 7.1, 7.1.2 and more. Dolby Digital Plus - a lossy compressed audio format found on most internet streaming content services and is capable of carrying Dolby Atmos. Dolby TrueHD - a lossless audio format found on UHD Blu-ray disc movies and is capable of carrying Dolby Atmos. Dolby ATMOS Atmos is not sound but information about sound and it rides in a container audio format. Atmos adds the ability to move sounds such that the sound can go from speaker to speaker across the room. The studio can create a more realistic sound field by implementing object based audio, allowing sound objects to phase out or in on different channels. Atmos adds ceiling or height speakers, 2, 4, or 6 and is the third number in the designation. So 7.1.2 is left front, right front, center, left rear, right rear, left surround, right surround, 1 subwoofer and left and right ceiling or height speakers. The format is "x.y.z" where: • "x" is the number of channels or speakers at or near ear level, • "y" is the number of channels or speakers dedicated to low bass reproduction • "z" is the number of overhead channels or speakers. If a system does not have any dedicated height channels, then the last digit is left off. 1.0 - this is a monophonic sound system with just one speaker reproducing all of the sound 2.0 - this is a standard "stereo system" - it has two speakers, left and right, to reproduce a stereo soundfield 2.1 - this represents a standard stereo system, but it adds a dedicated speaker for low bass reproduction (a woofer or subwoofer) 3.0 - this is similar to a stereo system, but it adds a dedicated center speaker between the front left and right speakers (many soundbars have this setup) 3.1 - as above, but with a dedicated bass speaker (subwoofer) 4.0 - A typical 4.0-channel system uses two speakers in the front and two in the rear or side to reproduce surround sound 4.1 - as above, but with a dedicated bass speaker 5.0 - this is typically used to describe a traditional surround sound system with three speakers across the front (front left, center and front right) and two speakers on the sides or in the rear to generate surround sound 5.1 - as above, but with a dedicated bass channel or subwoofer (Dolby Digital) 7.0 - this type of system has three speakers in the front, 2 on the side (side surround) and 2 in the rear (rear surround) 7.1 - as above, but with a dedicated bass channel or speaker 5.1.2 - this is a "standard" 5.1-channel surround sound system, with the addition of two height channel or speakers that generate sound from above the listener 5.1.4 - as above but with 4 height channels or speakers to generate sound above the listener 7.1.2 - a standard 7.1-channel system with two additional speakers dedicated to reproducing sound above the listener 7.1.4 - as above, but with 4 height channels or speakers 7.2.4 - as above, but with 2 dedicated bass speakers (subwoofer) 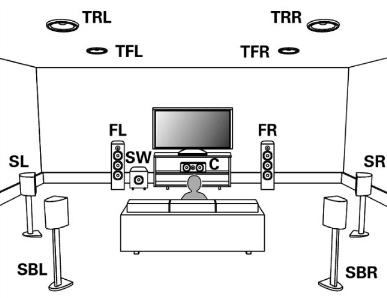 Dolby ATMOS speaker setup Can I get Dolby ATMOS with a soundbar? The best surround sound reproduction will be achieved using an Audio/Video Receiver (AVR) with dedicated channels however many soundbars are being made with additional height speakers in them in an attempt to add an ATMOS style sound field. Dolby ATMOS AVR  7.2.4 seven front and surround speakers and two bass speakers capability plus 4 height speakers. The 4 speaker connections on the far right are for height speakers. Older sound systems Dolby Surround Pro-Logic emerged in home theater systems in the early 1990's. It became the surround sound standard for Hi-Fi VHS, and is still the standard for today's analog TV broadcasts, since the Dolby Surround Pro-Logic signal can be encoded in a stereo analog signal. If you have an "older" Dolby Surround Pro-Logic receiver, you can still enjoy movies from DVD-Video, since all DVD-Video players down-mixes the Dolby Digital information to the Dolby Surround Pro-Logic format, and outputs the signal as a stereo audio pair. Extended Surround
formats: Just
when you thought 5.1-channel Dolby Digital and DTS surround sound were
enough, there are two more "Extended Surround" formats, namely THX
Surround EX™ and DTS
Extended Surround™ (or
DTS-ES™ for short). THX
Surround EX is the Extended Surround version of Dolby Digital 5.1,
while DTS-ES is that of DTS 5.1. The
difference between the new
Extended Surround formats and their 5.1-channel surround sound
counterparts is the addition of a surround
back channel,
whose corresponding speaker is placed behind
the audience. This allows certain soundtrack effects to be
presented behind the audience, thereby achieving more enveloping and
complete 360° surround sound. (Remember that in the
5.1-channel surround sound formats, the surround speakers are placed
one on each side of the audience - not behind them.)
Additionally, while the Extended Surround
sound format
calls for one surround back channel, two surround back speakers are
generally recommended for better envelopment. Acknowledging
this widely accepted industry position, some high-end receiver
manufacturers have introduced "7.1-channel" capable receivers, with
decoding and sometimes amplification for the two extra surround back
channels. A true 6.1-channel format: DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 DTS-ES can optionally support a fully discrete surround back channel. That is, the surround back channel has it own data stream and is truly independent from those of the surround left and surround right channels. This true 6.1-channel format is appropriately called DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 (in contrast to its matrix counterpart, DTS-ES Matrix). And as with DTS-ES Matrix, this discrete format is better realized with two surround back speakers. The Extended Surround formats are completely backwards-compatible with their 5.1-channel counterparts. That is, THX Surround EX is backwards compatible with Dolby Digital 5.1, and DTS-ES Matrix and DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 are backwards compatible with DTS 5.1. Additionally, DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 is backwards compatible with DTS-ES Matrix. In order to hear the matrix Extended Surround formats, you will need a THX Surround EX, DTS-ES Matrix, or a generic "6.1-channel" decoder in your receiver or preamplifier and use the digital audio output of your DVD player. To hear DTS-ES Discrete 6.1, you will need a DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 decoder in your receiver or preamplifier. In any case, you will also need six or seven channels of amplification, and one or two extra speakers for the surround back channel. Rest assured, you can still use your existing (or a soon-to-be-purchased) DVD-Video player, as long as it features Dolby Digital and DTS digital output. Movies and DVDs featuring Extended Surround "Star Wars: Episode 1 The Phantom Menace" is the very first movie to feature Dolby Digital Surround EX format. The first DVD with THX Surround EX is "Austin Powers: The Spy Who Shagged Me", while the first with DTS-ES 6.1 Discrete is "The Haunting". "Terminator 2: Judgment Day (Ultimate Edition)" DVD features both THX Surround EX and DTS-ES Discrete 6.1. Proper use and placement of surround sound speakers are key to getting the most out of surround sound systems.• Bluray surround sound • Home Theater Surround Sound Columbia ISA Audio/Video Empowering consumers thru information. |