
 |
|
Internet - High Speed Wireless How to setup wireless Wi-Fi internet service Setting up wireless internet in the home is something that many are doing today and sometimes doing it all by themselves to save money. A modern laptop computer already has wireless built-in and smartphones also have wireless capability. Smart TV, Audio/Video Receivers and desktop computers all have wireless capability. The advantage of wireless is your device is free from wired cables, allowing you to go almost anywhere in the home. Wireless in the home You need a wireless router. The router connects to a cable modem or ONT (fiber optic) and you can also connect laptops, desktop PCs to the LAN Ethernet ports on the router's rear panel. Wireless routers are advancing each year in speed and performance. The router will have status indicator lights on the front so you can see if you have power and a connection.  Some wireless routers have external antennas which offer a more robust signal.  Wireless router rear panel 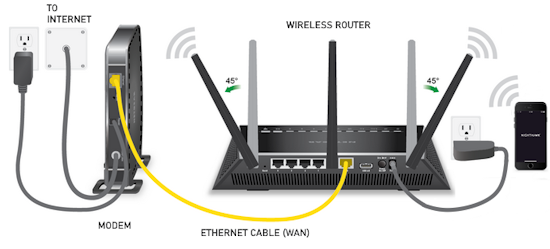 Wireless router connection diagram The WAN port (Wide Area Network) connects to a modem using Ethernet cable. The WAN port for the modem is usually color coded or labeled (Internet etc.). While the router connects devices wirelessly or wired, it must use a modem for data transfers from internet. The LAN ports (Local Area Network) are for connecting your devices such as laptops using an Ethernet cable. There are usually 4 LAN ports on the router. The IEEE 802.11 standard defines the protocols that enable communications with current wireless devices, including wireless routers. Sometimes a combo unit, wireless router and modem, are combined into a single box. What is a good router to buy? • Netgear Netgear.com • TP-Link TP-Link.com • ARRIS • Linksys Linksys.com Get started setting up wireless router 1. Get documentation Look for important setup information, like the router's default username and password. Often this information is printed directly on the router. 2. Check for an app Many router manufacturers now provide mobile apps or web browser dashboard interface that can be used for both setup and management of the router. With a smartphone app, you may not have to connect the router to a computer to configure it. Check the documentation that came with your router to see if an app is available. 3. Install and extend any external antennas on the router. Router setup steps Step 1: Decide where to place the router The best place for a wireless router is in an open central area. However, sometimes it's not easy to find a space out in the open because you must connect the router to a broadband gateway from your ISP (Internet service provider), which is usually attached to a cable near an outside wall. Step 2: Connect to your existing Internet setup (Modem) Attach the router to a cable (Ethernet)- or choose a mesh router. To solve the "long-distance" problem when connecting a router, you can use a CAT5e or CAT6 cable to connect the router to the ISP gateway's Ethernet port (Modem or ONT). Another option is to run Ethernet cables through the walls to the chosen central location for the router. Yet another option is to install a mesh network with a router. A mesh network allows you to place multiple Wi-Fi transmitters across your home or office, all on one network. Unlike extenders, which can be used with any wireless router, mesh networks require a router with this capability built-in. No matter which option you choose, you'll use a basic Ethernet cable, plugged into the router's wide-area network (WAN) or Internet port. The Internet port is typically set apart from other ports by a different color. Check the router's LED lights Your router's LED lights tell you if you've successfully made an active Internet connection. If you don't see lights confirming such a connection, make sure you've plugged the cable into the correct port and have power. Test the connection with a device Confirm that your router has a working connection by plugging a computer into one of the device ports on the back of the router. If all goes well, you should be able to begin a wired connection, just as you did when confirming an active Internet connection. Step 3: Configure the wireless router gateway In some cases, ISPs offer customers gateways with built-in routers. In most cases, these combined devices are not built for flexibility, nor do they have extra ports, security, and other options that allow you to add services and expand networks. If you have a gateway with an integrated router, you'll have to configure the gateway to disable the router and pass the WAN IP address—the unique Internet protocol address that the Internet provider assigns to your account—and all network traffic through to your new router. If you don’t take this step with a combo unit, you may run into conflicts that prevent devices from working properly. You may need to contact your ISP for help with this step. You can often obtain a standalone modem, plus you will save money by not paying extra for their router. Step 4: Connect gateway to router First, turn off the gateway. If there is already an Ethernet cable plugged into the gateway's local-area network (LAN) port, unplug the cable and plug it into your router's WAN port. Turn the gateway back on and wait a few minutes for it to boot up. Plug in the router's power supply and turn it on, again waiting a few minutes. Step 5: Use mobile app on your phone or web browser dashboard on your computer. The easiest way to continue with router setup is to use a mobile app if the router maker provided one. If there is no app, or you'd rather use the router's web-based dashboard, connect the router to a computer via an Ethernet cable. You might find the router's IP address printed on the back of device itself; if not, type 192.168.1.1, a common router address, into the web browser search bar. If that does not connect, try 192.168.1.0 or other like IP addresses. Step 6: Create a username and password To configure the router, you'll need to log in, using its default admin name and password. You can usually find this information printed on the router itself, or in an accompanying user manual. Next, enter the required credentials. Once you're in, you should immediately create a new username and password. The defaults are usually something like "admin" and "password," which are obviously not secure—so make sure to change them at the first opportunity. Step 7: Update the router's firmware Your router may need an update of the "firmware," or software that operates it. Update it as soon as possible, since the new firmware might fix bugs or offer new security protections. Some routers may download new firmware automatically, but many do not. You may need to check for updates through the app or the browser interface. Step 8: Create a Wi-Fi password Just as most routers come with preassigned admin usernames and passwords, most also come with preset Wi-Fi usernames and passwords. You’ll likely be prompted to change the Wi-Fi username and password, but even if you don't see such a prompt, plan to do so. The Wi-Fi password is different than the login password for the router. Step 9: Use auto-configuration tools where possible If your router is equipped with auto-install features, rely on them to help complete setup. For example, you should be able to use auto-configuration to manage IP addresses with the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), which automatically assigns IP addresses to devices. You can always change these addresses later. Step 10: Set up security Many router manufactures provide security functionality to safeguard network and user privacy. You can login into the web dashboard and enable added security features such as firewall, web filtering, and access controls to protect yourself from malicious traffic. Step 11: Test Wi-Fi connection Using a mobile phone or wireless laptop etc. configure the wireless network connection by turning on Wi-Fi and searching for your Wi-Fi network name. Enter the Wi-Fi password, connect and try a browser address to test internet connectivity. • How to Install a NETGEAR Wireless N-Router with Smart Wizard - YouTube Video - Older Router • How to Install Your Netgear Nighthawk WiFi Router with the Netgear Nighthawk App Internet Connection Check your local area to see which internet service providers offer service for you to access internet. There may be more than one provider and several different technologies with different speeds. Faster data speeds for download will allow streaming to TV. Internet access is needed for streaming movies, doing banking, bill pay, email, getting information and more. In the USA, 97% of homes access internet. There are at least five common ways to connect to internet besides mobile cellular phone. 1) DSL 2) Cable 3) Fiber optic 4) Cellular home 5) Satellite  Standard telephone wire • DSL uses existing telephone infrastructure to provide internet connectivity. It is widely available in many areas, especially urban and suburban locations. DSL uses the standard copper telephone line connection, is slow and is usually found only in rural areas where this is the only way available to connect. DSL is being phased out by the large providers (AT&T stopped offering new service in Oct 2020) but smaller local providers still offer service. Satellite internet may be an option for rural or remote areas.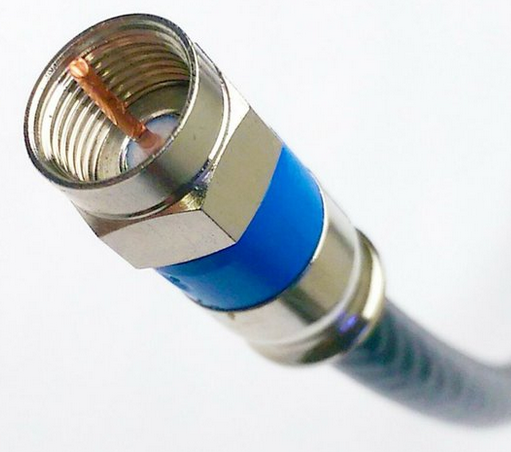  Coaxial cable • Cable internet uses coaxial cables that deliver cable television to provide internet connectivity. It is also widely available, particularly in urban and suburban areas. Cable uses a copper coaxial cable wire to connect to a cable service company and then on to internet. These cable companies started in the 1980s as a pay service for cable TV and have expanded to provide internet service over the already installed coaxial cable. The unused cable TV channels (frequencies) are used for internet while the normal cable TV channels are used for TV, both sent over the same cable to your home. At your home, a splitter is used to route signals to TV converter box or to modem. Currently around 50% of homes use cable.  Fiber Optical Cable • Fiber-optic internet, also known as fiber, offers the fastest and most reliable internet connections available. It utilizes thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light. Fiber internet is typically available in select urban areas, with coverage gradually expanding. Fiber optic is one of the newer methods to connect to internet and uses light (instead of electrical signals over copper wire) over a thin fiber optic cable. Often fiber optic cables are installed in addition to copper installs in a neighborhood but where copper cable is typically above ground, fiber is installed below ground meaning a trench is required to be dug to and around the neighborhood and also to the homes of consumers who sign up for the service. Known as microtrenching, a very narrow trench, up to 3 in. wide, is cut into the pavement, usually close to the seam, where the road meets the curb. Once the line is laid, a grout compound is used to fill in the trench. The seam is then sealed, which protects the line while restoring the integrity of the road surface. The depth of the trenches varies depending on the requirements. If fiber is available for your home and you sign up for service, your yard may be trenched and a terminal box attached to the home. Fiber comes into the home like copper cables through a junction box and distributed inside the home. Currently around 20% of homes use fiber but providers are heavily investing in the expansion of fiber. Duplex vs. Simplex Fiber Optic Patch Cables Simplex patch cable A simplex fiber optic cable has a single strand of glass or plastic fiber as its core and one single connector on each end. Simplex fiber cable is designed to either send or receive information through one-way transmission, but not send and receive at the same time. In addition, Simplex fiber optic cabling is excellent for long distance communication because it carries a single light ray at a time. Duplex patch cable A duplex fiber cable consists of two glass or plastic fiber strands with a double connector on each end. Duplex fiber cables provide two-way communication where separate transmit and receive lines require simultaneous bi-directional data transfer. PON means passive optical network GPON means Gigabit passive optical network  Cell Tower for home cellular internet • Cellular internet uses a router to connect to a provider's cellular network, just like a mobile phone. Cable, DSL and fiber optic internet require wires connecting your home to the provider's network. Fixed wireless services, like 5G, connect your home to a provider's network "over the air" using the provider's cellular network. Wi-Fi routers use short-range radio frequencies (typically either 2.4GHz or 5GHz) to transmit your internet signal to connected devices within your home. 5GHz might be one of the band options for your home's Wi-Fi system, but it's not the same as 5G, which is a cellular technology that uses higher-frequency waves. 5G home internet, on the other hand, is a fixed wireless internet service, which means that the connection between your provider and your home is not wired. With 5G, you will need an indoor or outdoor 5G receiver at your house to pick up the signal. It's similar to satellite internet, but instead of beaming in a signal from satellites, it's relaying information from a much closer wireless tower. Although you're using the same 5G network as your mobile phone, the gateway is specific to your location and cannot be used elsewhere. Costs can be less than cable or fiber. • Satellite internet access typically has used the 22,000 mile orbiting satellites which means slower speeds due to the distance the signals have to travel but now low Earth orbit satellites, only 800 miles away are being introduced (StarLink). 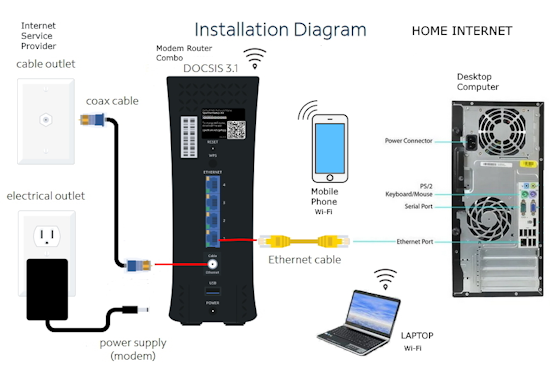 What is a modem and why do you need one for internet service The term “modem” is short for Modulator (Mo) Demodulator (Dem), which is what a modem does. In the case of a cable modem, modulation changes the properties of an analog radio frequency (RF) carrier wave to match the digital signals a modem receives through Ethernet. Demodulation works in reverse—it converts the RF carrier wave received from your internet service provider into digital signals your home network can use. The term “modem” primarily applies to cable, digital subscriber line (DSL), and satellite modems. Optical Fiber uses a different device called an optical network terminal (ONT). It still “modems,” but it deciphers light signals instead of radio waves. Why do you need a modem? Data from internet is already formatted for home network use on your ISP’s end, but generally, there are no Ethernet cables between you and your internet provider. So providers use several wired and wireless mediums to transfer data, like coax cables, telephone lines, and satellite communications from them to you. Fiber is also Ethernet-ready, but it uses lines with glass fibers instead of copper wires, requiring the use of an ONT. The internet backbone (main major communication lines) is all optical fiber, and your internet provider’s core network is most likely optical fiber. The differences generally come from the "last-mile" connection to your home. Translation is needed to get Ethernet-ready data across these various communication paths. Cable and DSL internet use RF carrier waves to send and receive data across copper wires. In both cases, providers modify the amplitude and phase of a radio wave to match the ones and zeros of a data wave. The modem receives the carrier wave and translates the modified shape into ones and zeroes (bits or computer data). Fiber internet also uses modulation and demodulation, but it utilizes laser or LED pulses instead of radio waves. For instance, a single pulse translates into a “one,” and no pulse equates to a “zero”—the two basic units of data. Moreover, these light pulses can reach 60 miles before they begin to degrade and need to be amplified. Ethernet uses a similar pulse method, but it relies on electrical pulses (signals) rather than light to send data between two points. This pulse method is one of the reasons fiber is better than cable, DSL, and satellite: It doesn’t use modified radio waves to transmit data, just a Morse code-like deciphering of pulses. A modem doesn’t require a router. You can connect your computer directly to the modem using Ethernet cable and get on the internet. No router is needed. Combination modem and router in one unit Providers just a few years ago rented their combo modem/router units which contain both a wireless router and a modem however with advancing technology and the desire by users to buy and configure their own routers to both save money and customize their home network, these combo units have fallen out of favor. Users can buy the latest router with faster speeds and save on the rental costs by just renting the modem. Remember that if the router you buy fails, you are responsible for replacement. Should I buy a modem or rent from my provider Buying a modem will cost about a year worth of rental costs so it will take you a year to break even. Then you start saving, however keep in mind that as technology advances, your provider may require an updated modem to be compatible. Your old modem may not work. Cable modems use standards such as DOCSIS 3.0 or 3.1 or 4.0 with 3.1 being current and 4.0 being introduced. Also, if your rented modem fails, your provider will replace it free while your purchased modem will require repair or replacement at your cost. What is DOCSIS? DOCSIS stands for “Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification.” It is a standard that allows data to be transferred over cable lines using an existing coaxial cable TV system. How is DOCSIS 3.1 faster? DOCSIS 3.1 is faster than DOCSIS 3.0, because of the advanced signal process techniques. The advanced techniques use a frequency spectrum and increases the available spectrum for transferring downstream and upstream data. It works by using a higher-order modulation to transfer data, which is more efficient. DOCSIS 3.1 is capable of 10 gigabits per second (Gbps) download speeds and 1-2 Gbps upload speeds. What is a router and why do you need one for wireless internet service A router is a device which allows multiple wired or wireless devices such as computers, phones, laptops to share your single internet connection going through your modem. The router is a hub to connect all these devices to the internet and possibly wirelessly. The router connects to the modem and your devices connect to the router wirelessly (Wi-Fi) or wired (Ethernet). So the router forms your local area network (LAN) while the modem is part of the Wide Area Network (WAN). The router needs a modem because the router cannot send or receive data directly from internet. Your local ISP (Internet Service Provider) has a modem you can rent or you can buy your own. Some modems have the router built-in and some are just a modem in which case you also need to get a wireless router. The modem connects your home to the ISP. The ISP is connected to the world wide web (internet). You pay the monthly cost for access and to rent the modem plus fees. Your provider will rent you a modem or you can buy your own but make sure it is compatible with your provider's network. You just need to connect and then configure the router. Basic Summary of step by step to setup wireless internet at home 1. Call your service provider to sign up for internet service. 2. Get your modem and all cables for connections. 3. Buy a wireless router if the modem is not a combo unit (modem and router) 4. Connect Modem to cable coming into the home. 5. Connect wireless router to modem using one ethernet (Cat 5 or Cat 6) cable. 6. Setup the wireless router. (Network name, Password, wireless security etc.) 7. For each computer you plan to use, setup for wireless connection. 8. Power on modem, router and computer and connect wirelessly to internet. High-speed Wireless Internet at home How to setup Wireless internet at home Broadband internet service is available from local internet service providers such as your cable TV company or phone company. Providers such as Comcast, Charter, Cox and Spectrum Cable offer broadband internet service. Cable TV providers and telephone providers offer multiple services including television, telephone and internet. Sometimes you can save monthly costs by getting all three services together in a bundle. Cable TV providers have been around for decades offering a coaxial cable connection into your residence for TV programming. Now this same coaxial cable, typically an RG-6 coax cable, can carry high-speed internet along with TV programs. You need to sign up for high-speed internet service with a provider. Broadband Internet will be offered at various speeds with increasing cost for faster data transfers. The provider may offer to send a staff worker out to your residence to install your hardware for a fee. If you are handy with current technologies, sometimes you can save cost by doing it all yourself. This is particularly true with cable TV companies. Telephone companies can sometimes get complicated and require a technical person to do the work. Basically you will get a cable modem (or DSL modem from telephone companies), signal splitter and connecting cables. Then you connect your computer to the modem. Connect using a wired (ethernet) cable. This allows internet connection but not wirelessly. To add wireless capability you connect the modem to a wireless router and your wireless capable computer to the wireless router which uses radio signals to send and receive data to/from your computer. The modem must be compatible with your provider's network, it cannot be just any modem. Your provider will give you their modem or you can buy one yourself if you are sure it will work. One advantage to using your provider's modem is that as technology changes, you can swap the old modem for a new one. Cable modems from your cable TV provider are not hard to install and many people can do it themselves. 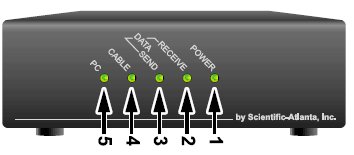 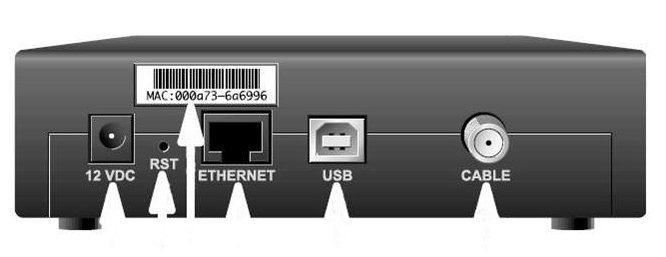 Cisco 2100 Cable Modem Front and Rear panels Combination internet and digital telephone Modems These modems have both telephone and internet connections. Your standard RJ-11 plug for landline phones and the RJ-45 ethernet connection plug into the rear of the modem which also has the coax cable connection.  Phone and Internet Cable Modem 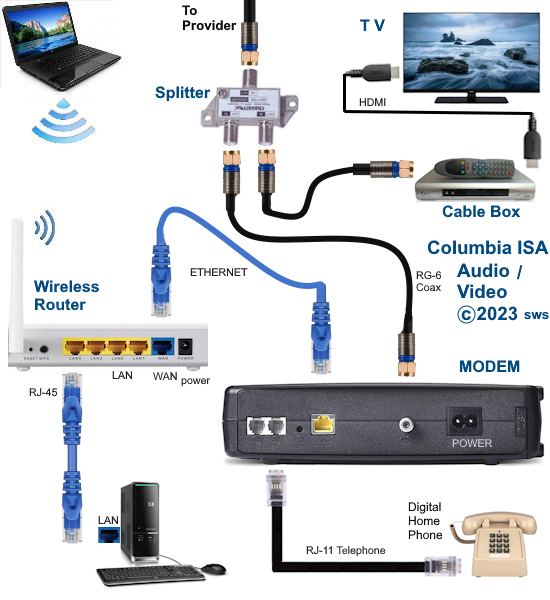 Diagram - TV, Internet and digital phone setup connection diagram More about Digital Phone Connecting a modem to your existing wiring is the first step towards going wireless. The modem manages data to/from your provider (your local cable TV company) and can connect to a wireless router for internet access anywhere in your home. Think of the modem as a bridge between your computer and the provider. The modem takes digital data from your computer and translates into the required signals the provider's system uses and also tunes in signals from the provider and translates into digital data for your computer. The cable modem actually looks for a specific TV channel coming across the coax cable. This channel is used for internet traffic instead of TV programming. Your provider has at their end another modem which has to take the signals from the coax cable and translate them into digital data and forward them to the internet. The modem plugs in to your house A/C wall outlet and will initialize on its own when powered on. Internet at home - Wireless Broadband from your cable company Your internet data and your TV signals travel over the same cable until split in your residence. A signal splitter takes the cable from your provider and splits one RG-6 cable into two. TV signals go over one RG-6 cable to your TV and internet data goes over the other cable to your modem, router and computer. Signal splitters are inexpensive and are usually provided when you signup for internet service with your local provider. The cable out of the splitter for internet data is connected to a cable modem. Again this small device is usually provided by your internet service provider. The cable modem has a port for the cable (RG-6) and a port for an ethernet (RJ-45) cable which connects to your computer or a router. You can connect a single computer using an ethernet cable or you can connect a router using an ethernet cable. The router allows multiple computers to use internet services and a wireless router allows multiple computers to locate around the house without wires and be on the internet. Most laptop computers today have built-in wireless adapters. USB wireless adapters are available for desktop computers. Broadband is fast and always on plus wireless gives you freedom from cable connections. Wireless routers are sold using a standard called IEEE 802.11 and as revisions and improvements are made, sometimes it is enough to rename a standard with a letter. So you will see IEEE 802.11b which is an older standard, 802.11g which has been current but has been upgraded to 802.11n in 2009. A Brief history of the wi-fi standard: In 1997, the IEEE ( Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) ratified the original 802.11 standard—the “802.11” technology term simply refers to Wi-Fi. In 1999 wireless was introduced to the general public with the 802.11 a and b ratifications. These standards had very low speeds (up to 54 Mbps & 11Mbps respectively). By 2003 some mobile devices that utilized Wi-Fi were available and portable laptops were becoming more standard for both business and personal use. 802.11g was ratified, delivering up to 54 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz space. The birth of the smartphone saw 802.11n come into play. The “n” standard brought about faster processing speeds of up to 450 Mbps for Wi-Fi and it supported both 2.4 Ghz and 5 Ghz devices. With demand growing, even faster speeds were needed. Enter Gigabit Wi-Fi. 802.11ac is the next advancement. The 802.11ac standard, also known as WiFi 5 and Gigabit WiFi, is the 5th generation of WiFi. It’s an upgrade from IEEE 802.11n, or WiFi 4. WiFi 5 was designed to deliver improved speeds, WiFi performance, and better range to keep up with the growing number of users, devices, and data. WiFi 6 is the next generation standard in WiFi technology. WiFi 6 also known as 802.11ax WiFi builds and improves on the 802.11ac WiFi standard. WiFi 7 is the upcoming WiFi standard, also known as IEEE 802.11be Extremely High Throughput (EHT). It works across all three bands (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz) to fully utilize spectrum resources. While WiFi 6 was built in response to the growing number of devices, WiFi 7's goal is to deliver astounding speeds for every device with greater efficiency. If you're struggling with constant buffering, lag, or congestion, a WiFi 7 router may be your best solution. Reading your Router Specifications: Supported - IEEE 802.11ac, IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11a and so you can see the router is compatible with previous standards. IEEE 802.11 Wireless Standards  Modem connections - Coaxial RG-6 cable from ISP and Ethernet cable connection. This modem does not have a router built-in. 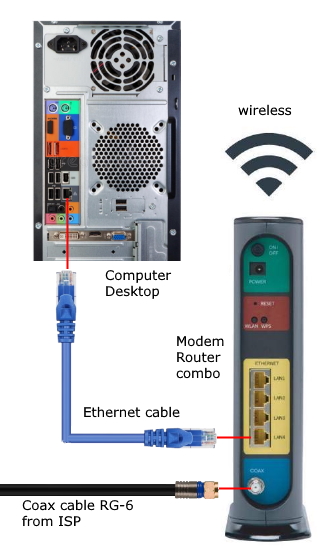 This modem has router built-in. Connections to computer so you can setup router. Ethernet, RJ-45 and LAN (local area network) all refer to basically the same connection. WAN refers to the ISP end. 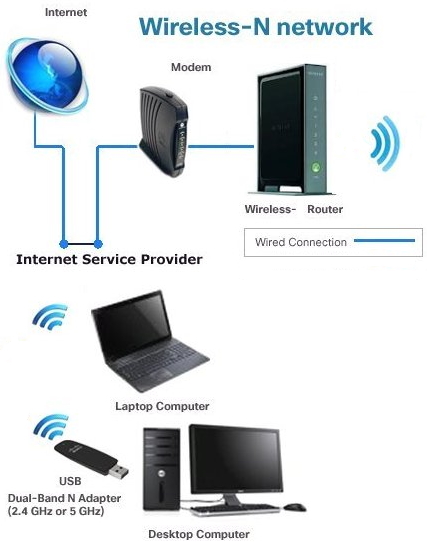 Setup diagram 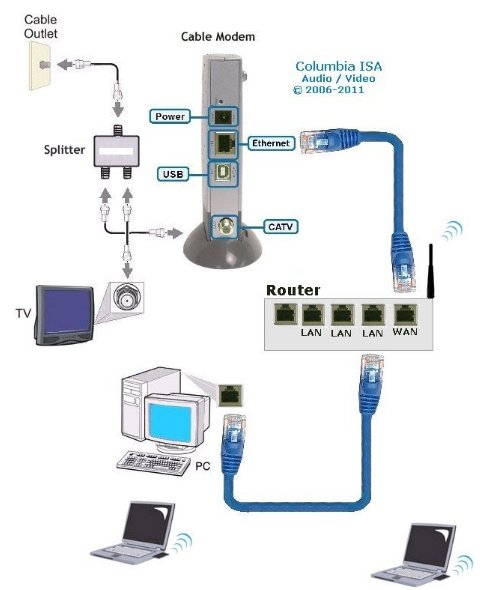 Basic diagram for wireless internet service in the home Ethernet cable - The cable connection from cable modem to router is done using an Ethernet cable. These cables are like the old telephone modular plugs, square looking plastic plug, only ethernet cables have more wires and have a bigger plug. Cables are not costly, 50 feet for $9 is common. Shorter cables can cost only a few dollars. Currently the standard to buy is called CAT6. Older ethernet cable standards were CAT5 and CAT5e.  Close-up of an Ethernet cable Wireless Routers Routers today are available from companies like Netgear, Belkin, Cisco/Linksys, D-Link, and others. Wireless routers operate at certain speeds and have features which allow you to fine-tune how you want your network to operate. Security is one aspect you need to address so that your signal will not be stolen by unauthorized users. Wireless routers operate in the 2.4GHz range of the radio spectrum with 5GHz being offered on some routers. Speed of data transfer to/from wireless routers are 54Mbps and faster. You can buy a new wireless router today for $50 with enough capability for all but the highest level of data transfers. If you want to stream HD video you may need to spend $80 for a top notch router. SETUP HOME NETWORK - WIRELESS Passwords Many people get confused about passwords because there are two different passwords when using home internet. 1. The password to login to the modem/router using your browser for the purpose of making changes to the modem/router. This password default is something simple such as "password" and is used with the login username such as "admin" but can be changed after you login to the modem/router. Look on the modem/router label to find the default user login name and default password. 2. The password to establish a wireless connection to the router using a device such as a TV or a mobile phone or a Blu-ray player. This password is associated with the network name or SSID and is created when the wireless router is setup and can be changed. This password is often called the "PreShared Key". • Getting Modem Router information After you hookup all the cables connecting modem, router and computer (ethernet) you need to power on the modem first and wait 2 mins. until the modem initializes and establishes communication with your provider. Next power on the router. The router will do the same as the modem so wait 1 to 2 mins. for it to come up to operational level. The router will have a wired connection available even if it is wireless, so you can connect your laptop/desktop computer using an ethernet wired cable. If you have Microsoft Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP or even Windows 2000 on your computer and you have current versions of Microsoft Internet Explorer or Firefox web browsers, you may notice that you can access the internet already. With the plug and play way todays software and hardware is setup, its easy to just go, it just works. However if you cannot access internet you may need to setup your computer for a broadband internet connection. For Windows computers, go into Control Panel, then Networks. You should see any defined network already setup and also see where you can create a NEW connection. 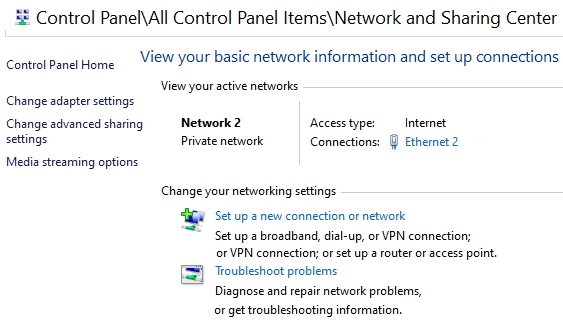 For broadband internet network already defined, you will want to click on it, then Properties and then Internet Protocol (TCPIP) and then Properties. 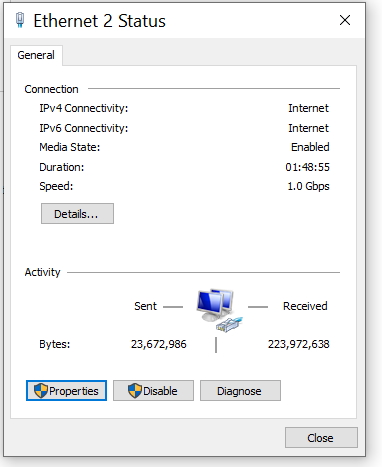 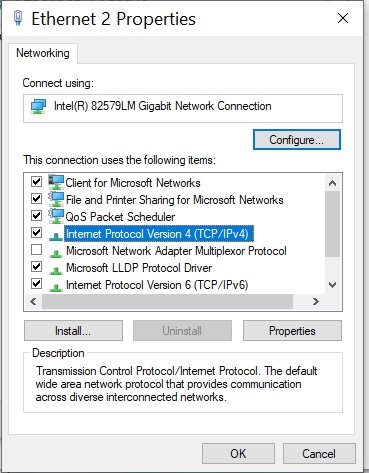 Next check Obtain IP Address automatically and also Obtain DNS server address automatically. Then click OK. 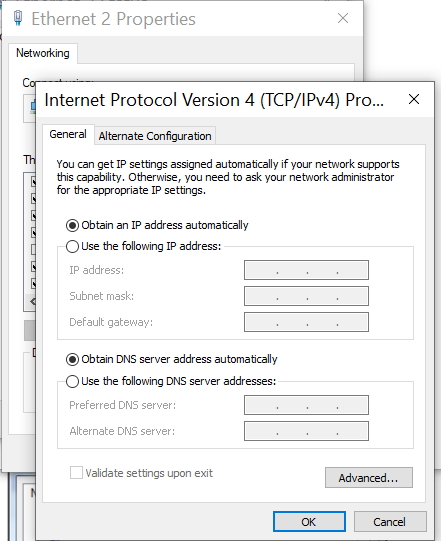 For Windows computers, you can go into command prompt (cmd) and enter the command ipconfig /all and you should see information including IP address of router, MAC address (physical address) etc. You can also PING the IP address of the router to see if you get a response. PING 192.168.0.1 You can logon to your router using your web browser to make changes to the router's configuration. Indeed you need to make some changes. Enter the IP address provided by the router manufacturer in the browsers address bar. Read owners manual for this address. Enter 192.168.1.1 is one example. Enter 192.168.0.0 is another example. 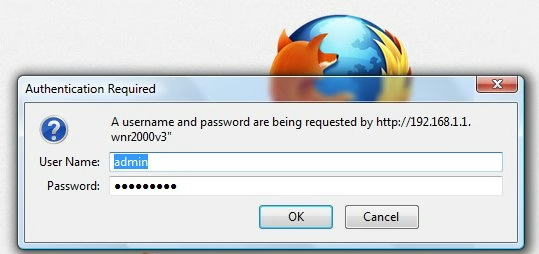 Router login using your web browser
Next logon with a user name and a password. admin is one example of a typical user name and password is one example of a default password. This logon password obviously needs to be changed to secure your router. Usually you get a menu of things you can change. The SSID is one item you should change. Also you need to change your router's security so that your signals cannot be used by unauthorized persons. 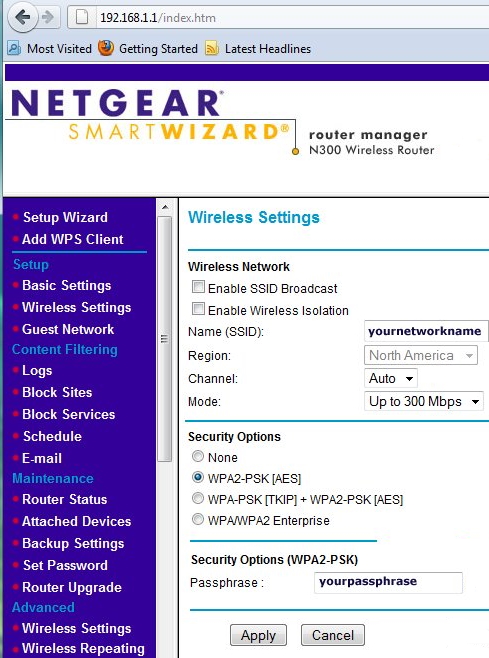 Change your SSID name to something of your choice. This name will be assigned to all network devices using your home network. It will also show up as the name of your network in a list of connectable networks whose signals are strong enough to be used (Wi-Fi). You can choose to not have the network name broadcast, adding additional security. Enter a passphrase of your choice. This will be used by any potential computer users to access your home network. If someone does not know your passphrase, they cannot typically use your network. Choose one of the security options to encrypt data (or choose none). WPA-PSK (TKIP), WPA2-PSK (AES). Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) using a pre-shared key to perform authentication and generate the initial data encryption keys. The very strong authentication along with dynamic per frame re-keying of WPA makes it virtually impossible to compromise. Wi-Fi security settings explained Security enabled networks are more difficult to use without authorization. Always click APPLY to save changes. Next click on SET PASSWORD and change the default password to administer your router. Write down your passphrase and password in a safe place so that you do not forget them over time. 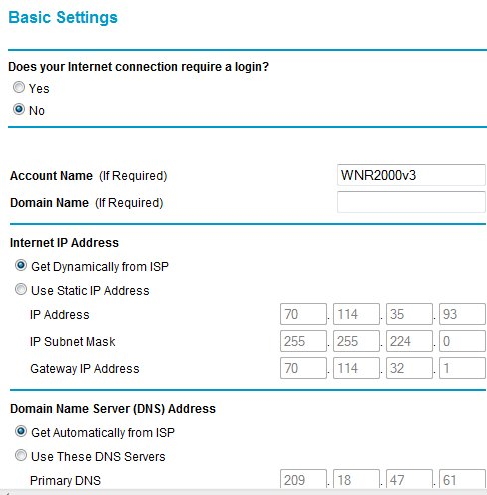 Most often you will check the Automatic / Dynamic option to get your IP address, both for the internet IP address and the DNS IP address. Your IP addresses are assigned automatically from your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Get HELP Sometimes things need to be tuned and configured in order to work. Call your provider if you cannot resolve problems as they should be able to assist you. Also, if you buy a wireless router, you can usually call the manufacturer's toll free number for help. Once your home network is setup, you can access it using media devices which have Wi-Fi capability. Go into the device's network setup menu and select AUTO or manually enter IP addresses. Often your network ID will show up as a choice for connection and you select your SSID and connect. Laptops with Windows Vista or Windows 7 will automatically connect to your SSID once you have connected the first time. This way you do not need to connect every time you use the laptop. HDTVs and Blu-ray players now have built-in Wi-Fi for internet connectivity. Go into Settings, then Network, select wireless and AUTO. Often it is that easy to get connected to the internet. Router setup How to Set Up a Wireless RouterSet Up Your Wireless Router on a Windows PC 1. Connect the wireless router to the modem using an Ethernet (CAT 6) cable. In the case of a modem/router combo unit, this is not required. 2. Connect the wireless router to a power source. Wait two minutes, and then continue to the next step. 3. Click the network icon in the Windows PC notification area. 4. Select your wireless network from the list of available networks to complete the setup process. By default, your network name will be the name of your router manufacturer. You can either setup the router with A: or B: below. A: Set Up Your Router Using the Setup Software 1. Make sure that your wireless router is completely disconnected from the modem, the computer, and the power source. 2. On your PC, insert the disc that came with your router, or download and run the latest version of the router's software from the vendor website. 3. Follow the on-screen instructions. The setup routine will ask you to connect components (including your modem and PC) in a certain order, and it may request that you temporarily connect your wireless router to a computer via an ethernet cable. You will also create a wireless network name and password at this point. B: Manually Configure Your Router Without Setup Software 1. Connect your wireless router to the modem, using an Ethernet cable. 2. Connect the wireless router to a power source. Wait two minutes to ensure that your router is fully operational. 3. Connect the wireless router to your computer using an Ethernet cable. 4. Log in to your router’s Web interface by opening a browser and entering the IP address of your router into the address bar. The IP address should be listed within your router’s documentation; if you can't find it, most routers use a common IP address such as http://192.168.1.1, http://192.168.0.1, or http://192.168.2.1. 5. Enter the default username and password, which you should find within your router’s documentation or on the label on the router. 6. Use the Web interface to set up a network name and password. 7. Disconnect your computer from the wireless router and then reconnect wirelessly. Caution: Be sure to use a password to protect your wireless network. WiFi Internet Eliminates necessity of running LAN cable
Other Wireless Devices: SETUP BLU-RAY PLAYER with Wireless internet Once your home network is setup you can add other wireless devices such as a Blu-ray Player to access internet content. How does the Internet work? • See over 100 Hookup Diagrams • RF Modulators and DVD Connections. More options for video and audio connections. • Surround Sound over HDMI • How to hookup surround sound • Surround Sound Glossary • How to add great sound to HDTV - Sound Bar • home theater receiver • home theater in-a-box • Cable Guide • Routers • How to install cable/dsl modem • How to setup wireless USB adapter for a desktop PC • How to setup wireless Internet for Blu-ray Player • Surround Sound • Camcorder Formats • How to choose a Camcorder • HDMI Switch box • VCR Basics • HDTV • How to connect DVD player in 10 easy steps • HDTV Basic Setup COLUMBIA ISA - Audio / Video Empowering consumers through information. columbiaisa@yahoo.com |